Initial commit
3
LICENSE
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
|
||||
To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ or send
|
||||
a letter to Creative Commons, PO Box 1866, Mountain View, CA 94042, USA.
|
||||
95
README.md
@@ -1,2 +1,93 @@
|
||||
# ATtiny814-USB-PD-Adapter
|
||||
USB Type-C Power Delivery Trigger and Monitoring Board
|
||||
# USB PD Adapter based on ATtiny814 or compatible
|
||||
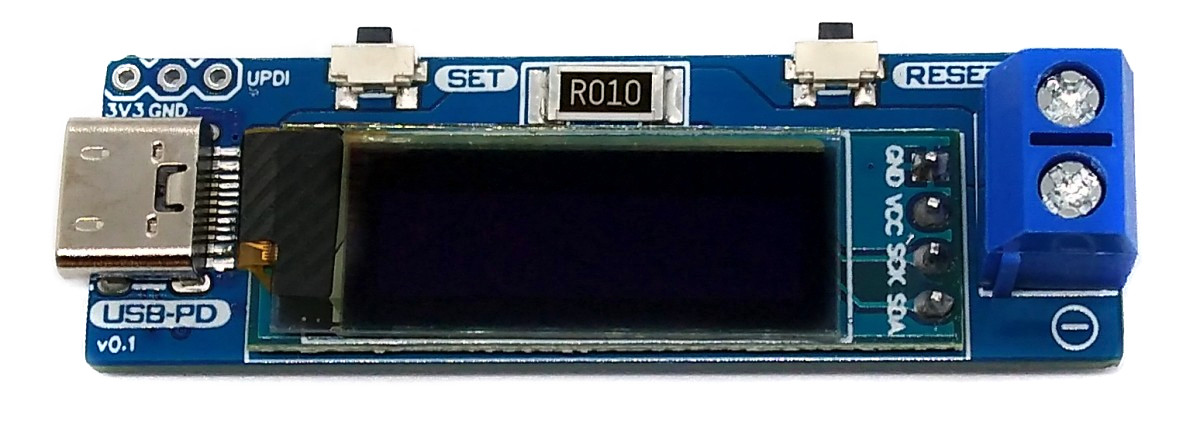
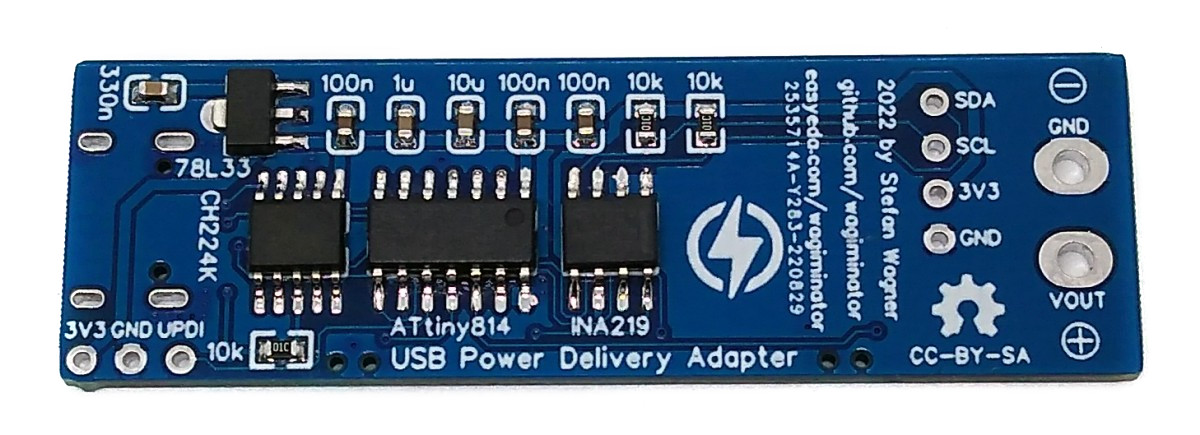
The USB PD Adapter is a USB Power Delivery trigger and monitoring board, with which you can use almost any USB Type-C PD power supply to power your projects with different selectable voltages and high currents. Important values such as voltage, current, power and energy are displayed on the OLED. The USB PD Adapter is based on the cheap and easy-to-use CH224K multi fast charging protocol power receiving chip, the INA219 voltage and current sensor IC, and an ATtiny204, 214, 404, 414, 804, 814, 1604 or 1614 microcontroller.
|
||||
|
||||
- Design Files (EasyEDA):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Hardware
|
||||
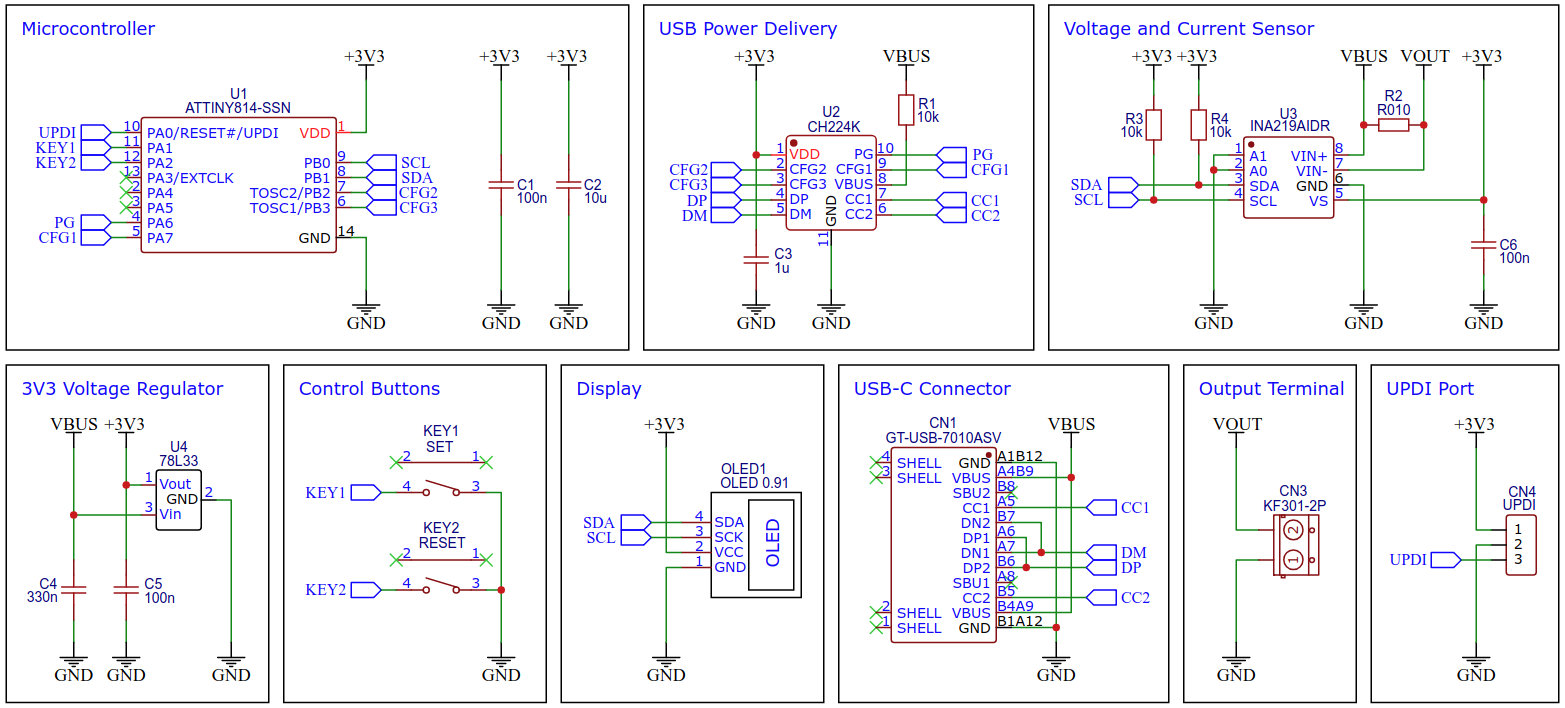
## Schematic
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
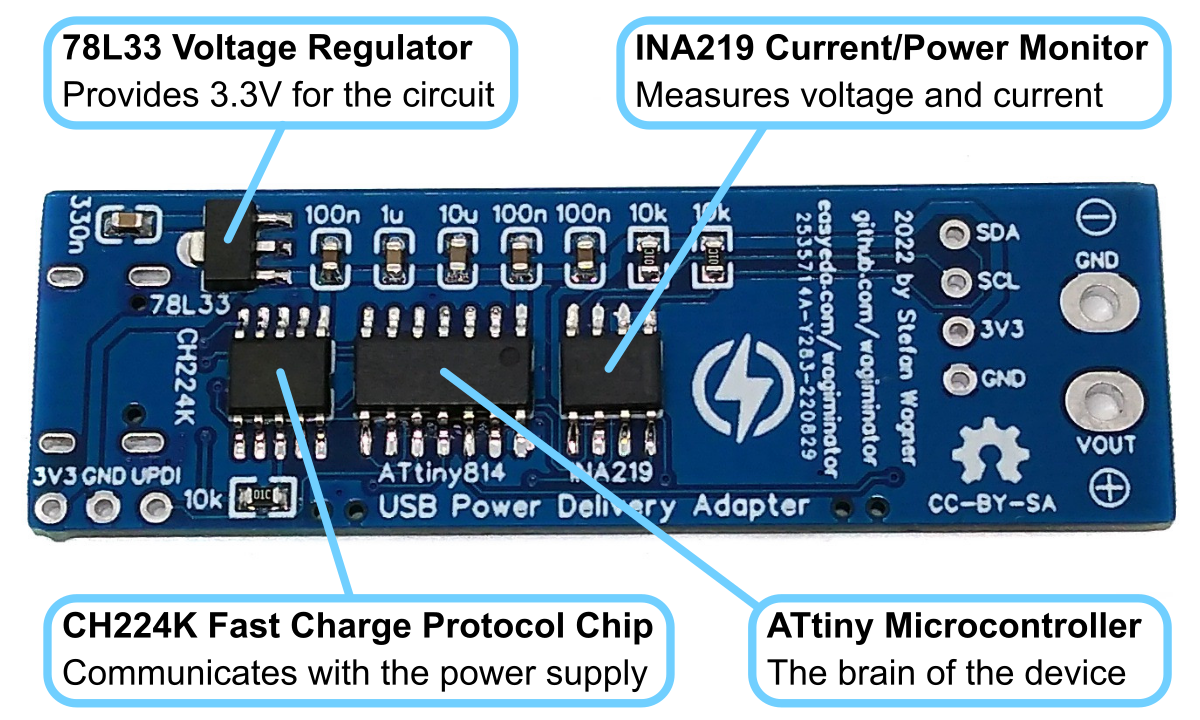
## 78L33 Voltage Regulator
|
||||
The 78L33 is a simple and inexpensive voltage regulator that can convert input voltages up to 30V to an output voltage of 3.3V with an output current of up to 200mA and a dropout voltage of 1.7V. The 78L33 supplies all elements of the circuit with 3.3V.
|
||||
|
||||
## CH224K USB PD Power Receiving Chip
|
||||
The CH224K is a USB PD power receiving protocol chip, which integrates PD3.0/2.0, BC1.2 and other fast charging protocols, automatically detects VCONN and analog E-Mark chips, supports up to 100W power, and has built-in PD communication module. It also integrates output voltage detection internally to support overheating and overvoltage protection. It features:
|
||||
|
||||
- 4V to 22V input voltage
|
||||
- PD3.0/2.0, BC1.2 and other fast charging protocols
|
||||
- USB Type-C PD, positive and negative insertion detection and automatic switching
|
||||
- E-Mark simulation, automatically detects VCONN, supports 100W power PD request
|
||||
- requested voltage can be dynamically adjusted through a variety of methods
|
||||
- high integration of single chip, simplified peripheral and low cost
|
||||
- built-in over-voltage and over-temperature protection module
|
||||
|
||||
The output voltage is selected via three configuration pins of the CH224K, which are connected directly to the ATtiny and is set according to the following table:
|
||||
|
||||
|Output Voltage|CFG1|CFG2|CFG3|
|
||||
|-|-|-|-|
|
||||
|5V|1|-|-|
|
||||
|9V|0|0|0|
|
||||
|12V|0|0|1|
|
||||
|15V|0|1|1|
|
||||
|20V|0|1|0|
|
||||
|
||||
The CH224K's PG pin is open-drain, pulling the input to ground when the requested voltage has been successfully negotiated with the USB PD power supply. It can be used to drive an indicator LED or a high-side P-channel MOSFET for power path control. Here this pin is connected directly to the ATtiny, which can query the status with the help of an internal pull-up resistor.
|
||||
|
||||
## INA219 Current/Power Monitor
|
||||
The INA219 is a current shunt and power monitor with an I²C-compatible interface. The device monitors both shunt voltage drop and bus supply voltage, with programmable conversion times and filtering. A programmable calibration value, combined with an internal multiplier, enables direct readouts of current in amperes. The selected shunt resistance of 10mΩ enables both a very small influence on the circuit and a measurement with a resolution of 1mA. For an accurate measurement, a shunt resistor with a low tolerance (1% or better) should be selected. The INA219 is used here to measure the output voltage and output current. It communicates with the ATtiny via I²C.
|
||||
|
||||
## ATtiny Microcontroller
|
||||
The ATtiny microcontroller handles the user interface, the control of the CH224K and INA219, and the calculation and display of the measured values. The user interface utilizes two buttons and an [SSD1306 128x64 pixels OLED display](http://aliexpress.com/wholesale?SearchText=128+64+0.96+oled+new+4pin). In this application, the ATtiny runs at only 1MHz to keep power consumption low and thus avoid overheating of the 78L33 voltage regulator, especially at 20V output voltage.
|
||||
|
||||
The following microcontrollers can be used: ATtiny204, 214, 404, 414, 804, 814, 1604 or 1614. However, since the firmware in the current version already requires almost 2KB of SRAM (depending on the compiler settings), the use of an ATtiny202 or ATtiny212 is not recommended, since there are hardly any reserves left for future upgrades.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Compiling and Uploading the Firmware
|
||||
## If using the Arduino IDE
|
||||
- Open your Arduino IDE.
|
||||
- Make sure you have installed [megaTinyCore](https://github.com/SpenceKonde/megaTinyCore).
|
||||
- Go to **Tools -> Board -> megaTinyCore** and select **ATtiny1614/1604/814/804/414/404/214/204**.
|
||||
- Go to **Tools** and choose the following board options:
|
||||
- **Chip:** choose the chip you have installed
|
||||
- **Clock:** 1 MHz internal
|
||||
- Leave the rest at the default settings.
|
||||
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the UPDI header on the board.
|
||||
- Go to **Tools -> Programmer** and select your UPDI programmer.
|
||||
- Go to **Tools -> Burn Bootloader** to burn the fuses.
|
||||
- Open the sketch and click **Upload**.
|
||||
|
||||
## If using the makefile (Linux/Mac)
|
||||
- Connect your [programmer](https://github.com/wagiminator/AVR-Programmer) (jtag2updi or SerialUPDI) to your PC and to the UPDI header on the board.
|
||||
- Download [AVR 8-bit Toolchain](https://www.microchip.com/mplab/avr-support/avr-and-arm-toolchains-c-compilers) and extract the sub-folders (avr, bin, include, ...) to /software/tools/avr-gcc. To do this, you have to register for free with Microchip on the download site.
|
||||
- Open a terminal.
|
||||
- Navigate to the folder with the makefile and the sketch.
|
||||
- Run `DEVICE=attiny814 PROGRMR=serialupdi PORT=/dev/ttyUSB0 make install` to compile, burn the fuses and upload the firmware (change DEVICE, PROGRMR and PORT accordingly).
|
||||
|
||||
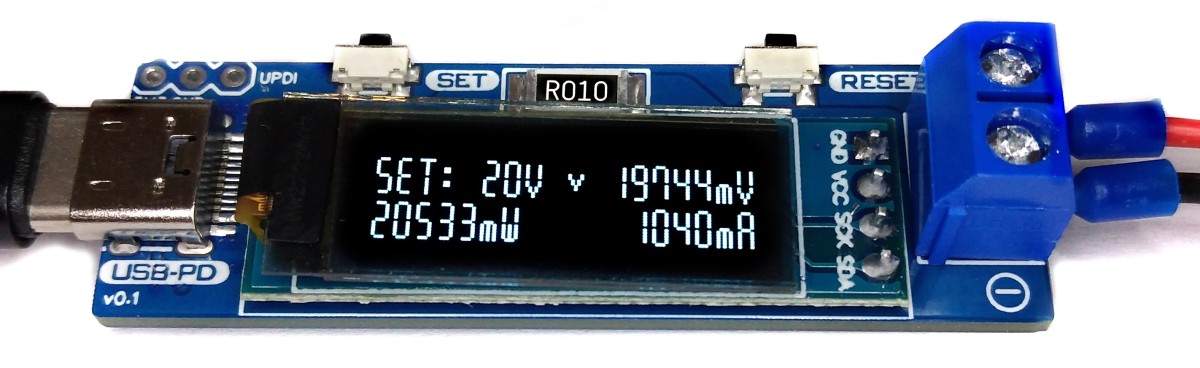
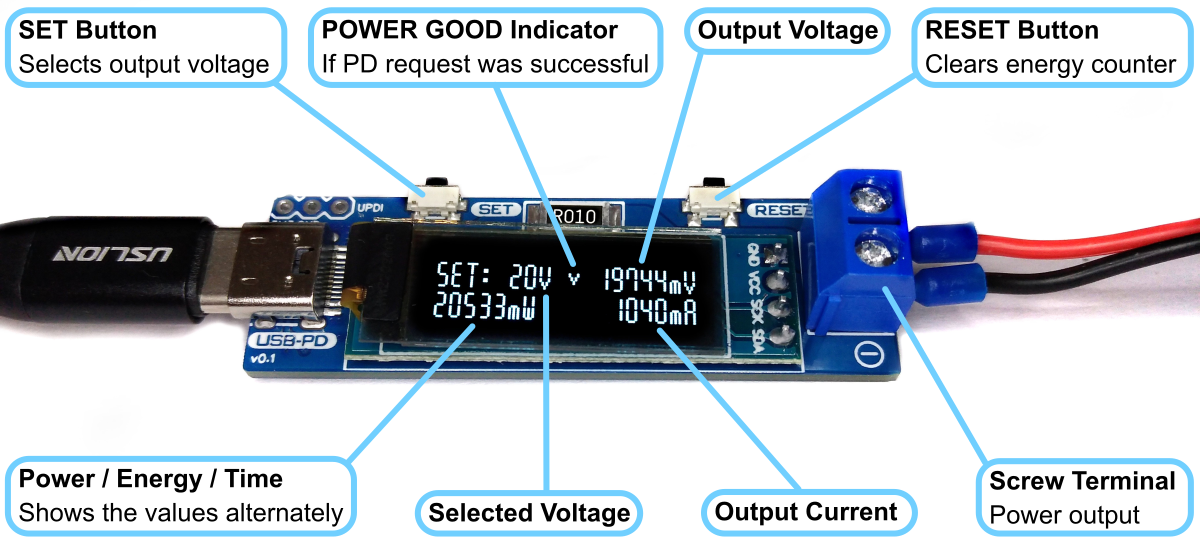
# Operating Instructions
|
||||
1. Connect the USB PD Adapter to a USB Type-C PD power supply using a USB-C cable.
|
||||
2. Use the SET button to select the desired output voltage. An hourglass appears on the display while the device is communicating with the power supply. If the negotiation was successful, a tick is displayed and the desired voltage is present at the output.
|
||||
3. Connect the device to the power consumer via the output screw terminal.
|
||||
4. Use the RESET button to clear the energy counter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# References, Links and Notes
|
||||
1. [78L33 Datasheet](https://datasheet.lcsc.com/lcsc/2204181745_Shikues-78L33_C2999140.pdf)
|
||||
2. [CH224K Datasheet](https://datasheet.lcsc.com/lcsc/2204251615_WCH-Jiangsu-Qin-Heng-CH224K_C970725.pdf)
|
||||
3. [INA219 Datasheet](https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/ina219.pdf?ts=1662832146107)
|
||||
4. [ATtiny814 Datasheet](https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/aemDocuments/documents/MCU08/ProductDocuments/DataSheets/ATtiny417-814-816-817-DataSheet-DS40002288A.pdf)
|
||||
5. [SSD1306 Datasheet](https://cdn-shop.adafruit.com/datasheets/SSD1306.pdf)
|
||||
6. [CH224K USB PD Decoy](https://github.com/wagiminator/Power-Boards/tree/master/USB-PD_Decoy_CH224K)
|
||||
7. [TI Primer on USB PD](https://www.ti.com/lit/wp/slyy109b/slyy109b.pdf)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
|
||||
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_hardware.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 891 KiB |
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_operation.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 411 KiB |
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_pic1.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 99 KiB |
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_pic2.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 111 KiB |
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_pic3.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 144 KiB |
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_pic4.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 127 KiB |
BIN
documentation/USB_PD_Adapter_wiring.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 161 KiB |
BIN
hardware/USB_PD_Adapter_BOM.tsv
Normal file
|
BIN
hardware/USB_PD_Adapter_gerber.zip
Normal file
6141
hardware/USB_PD_Adapter_schematic.pdf
Normal file
526
software/USB_PD_Adapter.ino
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,526 @@
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// Project: USB PD Adapter
|
||||
// Version: 1.0
|
||||
// Year: 2022
|
||||
// Author: Stefan Wagner
|
||||
// Github: https://github.com/wagiminator
|
||||
// EasyEDA: https://easyeda.com/wagiminator
|
||||
// License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Description:
|
||||
// ------------
|
||||
// With the USB PD Adapter you can use almost any USB Type-C PD power supply to power
|
||||
// your projects with different selectable voltages and high currents. Important
|
||||
// values such as voltage, current, power and energy are displayed on the OLED.
|
||||
// The USB PD Adapter is based on the cheap and easy-to-use CH224K multi fast
|
||||
// charging protocol power receiving chip, the INA219 voltage and current sensor IC,
|
||||
// and an ATtiny204, 214, 404, 414, 804, 814, 1604 or 1614 microcontroller.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Wiring:
|
||||
// -------
|
||||
// +-\/-+
|
||||
// Vcc 1|° |14 GND
|
||||
// --- !SS AIN4 PA4 2| |13 PA3 AIN3 SCK ----
|
||||
// ------- AIN5 PA5 3| |12 PA2 AIN2 MISO --- KEY2
|
||||
// CH224K PG --- DAC AIN6 PA6 4| |11 PA1 AIN1 MOSI --- KEY1
|
||||
// CH224K CFG1 ------- AIN7 PA7 5| |10 PA0 AIN0 UPDI --- UPDI
|
||||
// CH224K CFG3 -------- RXD PB3 6| |9 PB0 AIN11 SCL --- INA219/OLED
|
||||
// CH224K CFG2 ---------TXD PB2 7| |8 PB1 AIN10 SDA --- INA219/OLED
|
||||
// +----+
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Compilation Settings:
|
||||
// ---------------------
|
||||
// Core: megaTinyCore (https://github.com/SpenceKonde/megaTinyCore)
|
||||
// Board: ATtiny1614/1604/814/804/414/404/214/204
|
||||
// Chip: choose the chip you have installed
|
||||
// Clock: 1 MHz internal
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Leave the rest on default settings. Don't forget to "Burn bootloader"!
|
||||
// Compile and upload the code.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// No Arduino core functions or libraries are used. To compile and upload without
|
||||
// Arduino IDE download AVR 8-bit toolchain at:
|
||||
// https://www.microchip.com/mplab/avr-support/avr-and-arm-toolchains-c-compilers
|
||||
// and extract to tools/avr-gcc. Use the makefile to compile and upload.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Fuse Settings: 0:0x00 1:0x00 2:0x01 4:0x00 5:0xC5 6:0x04 7:0x00 8:0x00
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Operating Instructions:
|
||||
// -----------------------
|
||||
// 1. Connect the USB PD Adapter to a USB Type-C PD power supply using a USB-C cable.
|
||||
// 2. Use the SET button to select the desired output voltage. An hourglass appears
|
||||
// on the display while the device is communicating with the power supply. If
|
||||
// the negotiation was successful, a tick is displayed and the desired voltage
|
||||
// is present at the output.
|
||||
// 3. Connect the device to the power consumer via the output screw terminal.
|
||||
// 4. Use the RESET button to clear the energy counter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// Libraries, Definitions and Macros
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
// Libraries
|
||||
#include <avr/io.h> // for GPIO
|
||||
#include <avr/interrupt.h> // for interrupts
|
||||
#include <util/delay.h> // for delays
|
||||
|
||||
// Pin definitions
|
||||
#define PIN_SCL PB0 // I2C SCL, connected to INA219 and OLED
|
||||
#define PIN_SDA PB1 // I2C SDA, connected to INA219 and OLED
|
||||
#define PIN_CFG1 PA7 // CFG1 of CH224K
|
||||
#define PIN_CFG2 PB2 // CFG2 of CH224K
|
||||
#define PIN_CFG3 PB3 // CFG3 of CH224K
|
||||
#define PIN_PG PA6 // Power Good of CH224K
|
||||
#define PIN_KEY1 PA1 // Key 1
|
||||
#define PIN_KEY2 PA2 // Key 2
|
||||
|
||||
// Pin manipulation macros
|
||||
enum {PA0, PA1, PA2, PA3, PA4, PA5, PA6, PA7, PB0, PB1, PB2, PB3}; // enumerate pin designators
|
||||
#define pinInput(x) (&VPORTA.DIR)[((x)&8)>>1] &= ~(1<<((x)&7)) // set pin to INPUT
|
||||
#define pinOutput(x) (&VPORTA.DIR)[((x)&8)>>1] |= (1<<((x)&7)) // set pin to OUTPUT
|
||||
#define pinLow(x) (&VPORTA.OUT)[((x)&8)>>1] &= ~(1<<((x)&7)) // set pin to LOW
|
||||
#define pinHigh(x) (&VPORTA.OUT)[((x)&8)>>1] |= (1<<((x)&7)) // set pin to HIGH
|
||||
#define pinToggle(x) (&VPORTA.IN )[((x)&8)>>1] |= (1<<((x)&7)) // TOGGLE pin
|
||||
#define pinRead(x) ((&VPORTA.IN)[((x)&8)>>1] & (1<<((x)&7))) // READ pin
|
||||
#define pinDisable(x) (&PORTA.PIN0CTRL)[(((x)&8)<<2)+((x)&7)] |= PORT_ISC_INPUT_DISABLE_gc
|
||||
#define pinPullup(x) (&PORTA.PIN0CTRL)[(((x)&8)<<2)+((x)&7)] |= PORT_PULLUPEN_bm
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// I2C Master Implementation (Read/Write, Conservative)
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
#define I2C_FREQ 100000 // I2C clock frequency in Hz
|
||||
#define I2C_BAUD ((F_CPU / I2C_FREQ) - 10) / 2; // simplified BAUD calculation
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C init function
|
||||
void I2C_init(void) {
|
||||
TWI0.MBAUD = I2C_BAUD; // set TWI master BAUD rate
|
||||
TWI0.MCTRLA = TWI_ENABLE_bm; // enable TWI master
|
||||
TWI0.MSTATUS = TWI_BUSSTATE_IDLE_gc; // set bus state to idle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C start transmission
|
||||
void I2C_start(uint8_t addr) {
|
||||
TWI0.MADDR = addr; // start sending address
|
||||
while(!(TWI0.MSTATUS&(TWI_WIF_bm|TWI_RIF_bm))); // wait for transfer to complete
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C restart transmission
|
||||
void I2C_restart(uint8_t addr) {
|
||||
I2C_start(addr); // start sending address
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C stop transmission
|
||||
void I2C_stop(void) {
|
||||
TWI0.MCTRLB = TWI_MCMD_STOP_gc; // send stop condition
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C transmit one data byte to the slave, ignore ACK bit
|
||||
void I2C_write(uint8_t data) {
|
||||
TWI0.MDATA = data; // start sending data byte
|
||||
while(~TWI0.MSTATUS & TWI_WIF_bm); // wait for transfer to complete
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// I2C receive one data byte from slave; ack=0: last byte, ack>0: more bytes to follow
|
||||
uint8_t I2C_read(uint8_t ack) {
|
||||
while(~TWI0.MSTATUS & TWI_RIF_bm); // wait for transfer to complete
|
||||
uint8_t data = TWI0.MDATA; // get received data byte
|
||||
if(ack) TWI0.MCTRLB = TWI_MCMD_RECVTRANS_gc; // ACK: read more bytes
|
||||
else TWI0.MCTRLB = TWI_ACKACT_NACK_gc; // NACK: this was the last byte
|
||||
return data; // return received byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// INA219 Implementation
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 register values
|
||||
#define INA_ADDR 0x80 // I2C write address of INA219
|
||||
#define INA_CONFIG 0b0010011111111111 // INA config register according to datasheet
|
||||
#define INA_CALIB 4096 // INA calibration register according to R_SHUNT
|
||||
#define INA_REG_CONFIG 0x00 // INA configuration register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_CALIB 0x05 // INA calibration register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_SHUNT 0x01 // INA shunt voltage register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_VOLTAGE 0x02 // INA bus voltage register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_POWER 0x03 // INA power register address
|
||||
#define INA_REG_CURRENT 0x04 // INA current register address
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 write a register value
|
||||
void INA_write(uint8_t reg, uint16_t value) {
|
||||
I2C_start(INA_ADDR); // start transmission to INA219
|
||||
I2C_write(reg); // write register address
|
||||
I2C_write(value >> 8); // write register content high byte
|
||||
I2C_write(value); // write register content low byte
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 read a register
|
||||
uint16_t INA_read(uint8_t reg) {
|
||||
uint16_t result; // result variable
|
||||
I2C_start(INA_ADDR); // start transmission to INA219
|
||||
I2C_write(reg); // write register address
|
||||
I2C_restart(INA_ADDR | 0x01); // restart for reading
|
||||
result = (uint16_t)(I2C_read(1) << 8) | I2C_read(0); // read register content
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
return result; // return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 write inital configuration and calibration values
|
||||
void INA_init(void) {
|
||||
INA_write(INA_REG_CONFIG, INA_CONFIG); // write INA219 configuration
|
||||
INA_write(INA_REG_CALIB, INA_CALIB); // write INA219 calibration
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 read voltage
|
||||
uint16_t INA_readVoltage(void) {
|
||||
return((INA_read(INA_REG_VOLTAGE) >> 1) & 0xFFFC);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// INA219 read sensor values
|
||||
uint16_t INA_readCurrent(void) {
|
||||
uint16_t result = INA_read(INA_REG_CURRENT); // read current from INA
|
||||
if(result > 32767) result = 0; // ignore nagtive currents
|
||||
return result; // return result
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// OLED Implementation
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED definitions
|
||||
#define OLED_ADDR 0x78 // OLED write address
|
||||
#define OLED_CMD_MODE 0x00 // set command mode
|
||||
#define OLED_DAT_MODE 0x40 // set data mode
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED init settings
|
||||
const uint8_t OLED_INIT_CMD[] = {
|
||||
0xA8, 0x1F, // set multiplex for 128x32
|
||||
0x20, 0x01, // set vertical memory addressing mode
|
||||
0xDA, 0x02, // set COM pins hardware configuration to sequential
|
||||
0x8D, 0x14, // enable charge pump
|
||||
0xAF // switch on OLED
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED 5x16 font
|
||||
const uint8_t OLED_FONT[] = {
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x02, 0x20, 0x02, 0x20, 0x02, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 0 0
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 1 1
|
||||
0x00, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x00, // 2 2
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 3 3
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 4 4
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x00, 0x1F, // 5 5
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x00, 0x1F, // 6 6
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 7 7
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 8 8
|
||||
0x7C, 0x00, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // 9 9
|
||||
0x7C, 0x3F, 0x82, 0x00, 0x82, 0x00, 0x82, 0x00, 0x7C, 0x3F, // A 10
|
||||
0x7C, 0x03, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x30, 0x00, 0x0C, 0x7C, 0x03, // V 11
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x00, 0x20, 0x00, 0x3F, 0x00, 0x20, 0x7C, 0x1F, // W 12
|
||||
0x7C, 0x3F, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, // h 13
|
||||
0x00, 0x3F, 0x80, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3F, 0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x3F, // m 14
|
||||
0x7C, 0x1F, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x82, 0x20, 0x00, 0x00, // E 15
|
||||
0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, 0x7E, 0x3F, 0x02, 0x00, 0x02, 0x00, // T 16
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x30, 0x06, 0x30, 0x06, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, // : 17
|
||||
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, // 18 SPACE
|
||||
0x3E, 0x3E, 0x72, 0x39, 0xE2, 0x3C, 0x72, 0x39, 0x3E, 0x3E, // 19 hourglass
|
||||
0x60, 0x00, 0x80, 0x01, 0x00, 0x06, 0x80, 0x01, 0x60, 0x00 // 20 checkmark
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Character definitions
|
||||
#define COLON 17
|
||||
#define SPACE 18
|
||||
#define GLASS 19
|
||||
#define CHECK 20
|
||||
|
||||
// BCD conversion array
|
||||
const uint16_t DIVIDER[] = {1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000};
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED init function
|
||||
void OLED_init(void) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_CMD_MODE); // set command mode
|
||||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < sizeof(OLED_INIT_CMD); i++)
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_INIT_CMD[i]); // send the command bytes
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED set the cursor
|
||||
void OLED_setCursor(uint8_t xpos, uint8_t ypos) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_CMD_MODE); // set command mode
|
||||
I2C_write(0x22); // command for min/max page
|
||||
I2C_write(ypos); I2C_write(ypos+1); // min: ypos; max: ypos+1
|
||||
I2C_write(xpos & 0x0F); // set low nibble of start column
|
||||
I2C_write(0x10 | (xpos >> 4)); // set high nibble of start column
|
||||
I2C_write(0xB0 | (ypos)); // set start page
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED clear a line
|
||||
void OLED_clearLine(uint8_t ypos) {
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0, ypos); // set cursor at line start
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
uint8_t i = 0; // count variable
|
||||
do {I2C_write(0x00);} while(--i); // clear upper half
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED clear screen
|
||||
void OLED_clearScreen(void) {
|
||||
OLED_clearLine(0); OLED_clearLine(2); // clear both lines
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED plot a single character
|
||||
void OLED_plotChar(uint8_t ch) {
|
||||
ch = (ch << 1) + (ch << 3); // calculate position of character in font array
|
||||
I2C_write(0x00); I2C_write(0x00); // print spacing between characters
|
||||
I2C_write(0x00); I2C_write(0x00);
|
||||
for(uint8_t i=10; i; i--) I2C_write(OLED_FONT[ch++]); // print character
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print a character
|
||||
void OLED_printChar(uint8_t ch) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(ch); // plot the character
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print a "string"; terminator: 255
|
||||
void OLED_printStr(const uint8_t* p) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
while(*p < 255) OLED_plotChar(*p++); // plot each character of the string
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print value (BCD conversion by substraction method)
|
||||
void OLED_printVal(uint16_t value) {
|
||||
uint8_t digits = 5; // print 5 digits
|
||||
uint8_t leadflag = 0; // flag for leading spaces
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
while(digits--) { // for all digits digits
|
||||
uint8_t digitval = 0; // start with digit value 0
|
||||
uint16_t divider = DIVIDER[digits]; // read current divider
|
||||
while(value >= divider) { // if current divider fits into the value
|
||||
leadflag = 1; // end of leading spaces
|
||||
digitval++; // increase digit value
|
||||
value -= divider; // decrease value by divider
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!digits) leadflag++; // least digit has to be printed
|
||||
if(leadflag) OLED_plotChar(digitval); // print the digit
|
||||
else OLED_plotChar(SPACE); // or print leading space
|
||||
}
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OLED print 8-bit value as 2-digit decimal (BCD conversion by substraction method)
|
||||
void OLED_printDec(uint8_t value, uint8_t lead) {
|
||||
I2C_start(OLED_ADDR); // start transmission to OLED
|
||||
I2C_write(OLED_DAT_MODE); // set data mode
|
||||
uint8_t digitval = 0; // start with digit value 0
|
||||
while(value >= 10) { // if current divider fits into the value
|
||||
digitval++; // increase digit value
|
||||
value -= 10; // decrease value by divider
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(digitval) OLED_plotChar(digitval); // print first digit
|
||||
else OLED_plotChar(lead);
|
||||
OLED_plotChar(value); // print second digit
|
||||
I2C_stop(); // stop transmission
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// Millis Counter Implementation for TCB0
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
volatile uint32_t MIL_counter = 0; // millis counter variable
|
||||
|
||||
// Init millis counter
|
||||
void MIL_init(void) {
|
||||
TCB0.CCMP = (F_CPU / 1000) - 1; // set TOP value (period)
|
||||
TCB0.CTRLA = TCB_ENABLE_bm; // enable timer/counter
|
||||
TCB0.INTCTRL = TCB_CAPT_bm; // enable periodic interrupt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read millis counter
|
||||
uint32_t MIL_read(void) {
|
||||
cli(); // disable interrupt for atomic read
|
||||
uint32_t result = MIL_counter; // read millis counter
|
||||
sei(); // enable interrupt again
|
||||
return result; // return millis counter value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TCB0 interrupt service routine (every millisecond)
|
||||
ISR(TCB0_INT_vect) {
|
||||
TCB0.INTFLAGS = TCB_CAPT_bm; // clear interrupt flag
|
||||
MIL_counter++; // increase millis counter
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// CH224K Implementation
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
// Some variables
|
||||
enum {SET_5V, SET_9V, SET_12V, SET_15V, SET_20V};
|
||||
const uint8_t VOLTAGES[] = {5, 9, 12, 15, 20};
|
||||
uint8_t CH224K_volt = 0; // current voltage pointer
|
||||
|
||||
// Some macros
|
||||
#define CH224K_getVolt() (VOLTAGES[CH224K_volt]) // get voltage
|
||||
#define CH224K_isGood() (!pinRead(PIN_PG)) // power good?
|
||||
|
||||
// CH224K init
|
||||
void CH224K_init(void) {
|
||||
pinHigh(PIN_CFG1); // start with 5V
|
||||
pinOutput(PIN_CFG1); // CFG pins as output...
|
||||
pinOutput(PIN_CFG2);
|
||||
pinOutput(PIN_CFG3);
|
||||
pinPullup(PIN_PG); // pullup for Power Good pin
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CH224K set voltage
|
||||
void CH224K_setVolt(uint8_t volt) {
|
||||
CH224K_volt = volt;
|
||||
switch(CH224K_volt) { // set CFG pins according to voltage
|
||||
case SET_5V: pinHigh(PIN_CFG1); break;
|
||||
case SET_9V: pinLow (PIN_CFG1); pinLow (PIN_CFG2); pinLow (PIN_CFG3); break;
|
||||
case SET_12V: pinLow (PIN_CFG1); pinLow (PIN_CFG2); pinHigh(PIN_CFG3); break;
|
||||
case SET_15V: pinLow (PIN_CFG1); pinHigh(PIN_CFG2); pinHigh(PIN_CFG3); break;
|
||||
case SET_20V: pinLow (PIN_CFG1); pinHigh(PIN_CFG2); pinLow (PIN_CFG3); break;
|
||||
default: break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CH224K set next voltage
|
||||
void CH224K_nextVolt(void) {
|
||||
if(++CH224K_volt > SET_20V) CH224K_volt = SET_5V; // next voltage
|
||||
switch(CH224K_volt) { // change pins according to voltage
|
||||
case SET_5V: pinHigh(PIN_CFG1); pinLow(PIN_CFG2); break;
|
||||
case SET_9V: pinLow (PIN_CFG1); break;
|
||||
case SET_12V: pinHigh(PIN_CFG3); break;
|
||||
case SET_15V: pinHigh(PIN_CFG2); break;
|
||||
case SET_20V: pinLow (PIN_CFG3); break;
|
||||
default: break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
// Main Function
|
||||
// ===================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
// Some "strings"
|
||||
const uint8_t mA[] = { 14, 10, 255 }; // "mA"
|
||||
const uint8_t mV[] = { 14, 11, 255 }; // "mV"
|
||||
const uint8_t mW[] = { 14, 12, 18, 255 }; // "mW "
|
||||
const uint8_t Ah[] = { 10, 13, 18, 255 }; // "Ah "
|
||||
const uint8_t mAh[] = { 14, 10, 13, 255 }; // "mAh"
|
||||
const uint8_t Wt[] = { 12, 18, 18, 255 }; // "W "
|
||||
const uint8_t Wh[] = { 12, 13, 18, 255 }; // "Wh "
|
||||
const uint8_t mWh[] = { 14, 12, 13, 255 }; // "mWh"
|
||||
const uint8_t SET[] = { 5, 15, 16, 17, 18, 255 }; // "SET: "
|
||||
const uint8_t HGL[] = { 11, SPACE, GLASS, SPACE, 255}; // hourglass
|
||||
const uint8_t CMK[] = { 11, SPACE, CHECK, SPACE, 255}; // checkmark
|
||||
const uint8_t SEP[] = { SPACE, SPACE, SPACE, 255}; // seperator
|
||||
|
||||
// Main function
|
||||
int main(void) {
|
||||
// Setup
|
||||
_PROTECTED_WRITE(CLKCTRL.MCLKCTRLB, 7); // set clock frequency to 1 MHz
|
||||
CH224K_init(); // init CH224K
|
||||
I2C_init(); // init I2C
|
||||
INA_init(); // init INA219
|
||||
OLED_init(); // init OLED
|
||||
MIL_init(); // init TCB for millis counter
|
||||
sei(); // enable interrupts
|
||||
pinPullup(PIN_KEY1); pinPullup(PIN_KEY2); // pullup for keys
|
||||
OLED_clearScreen(); // clear OLED
|
||||
|
||||
// Local variables
|
||||
uint16_t volt, curr; // voltage in mV, current in mA
|
||||
uint32_t power; // power in mW
|
||||
uint32_t energy = 0, charge = 0; // counter for energy and charge
|
||||
uint32_t interval, nowmillis, lastmillis = 0; // for timing calculation in millis
|
||||
uint32_t duration = 0; // total duration in ms
|
||||
uint16_t seconds = 0; // total duration in seconds
|
||||
uint8_t lastkey1 = 0, lastkey2 = 0; // for key pressed dectection
|
||||
|
||||
// Loop
|
||||
while(1) { // loop until forever
|
||||
// Read sensor values
|
||||
volt = INA_readVoltage(); // read voltage in mV from INA219
|
||||
curr = INA_readCurrent(); // read current in mA from INA219
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate timings
|
||||
nowmillis = MIL_read(); // read millis counter
|
||||
interval = nowmillis - lastmillis; // calculate recent time interval
|
||||
lastmillis = nowmillis; // reset lastmillis
|
||||
duration += interval; // calculate total duration in millis
|
||||
seconds = duration / 1000; // calculate total duration in seconds
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate power, capacity and energy
|
||||
power = (uint32_t)volt * curr / 1000; // calculate power in mW
|
||||
energy += interval * power / 3600; // calculate energy in uWh
|
||||
charge += interval * curr / 3600; // calculate charge in uAh
|
||||
|
||||
// Check SET button
|
||||
if(pinRead(PIN_KEY1)) lastkey1 = 0;
|
||||
else if(!lastkey1) {
|
||||
CH224K_nextVolt();
|
||||
lastkey1++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Check RESET button
|
||||
if(pinRead(PIN_KEY2)) lastkey2 = 0;
|
||||
else if(!lastkey2) {
|
||||
duration = 0; seconds = 0; energy = 0; charge = 0;
|
||||
lastkey2++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Display values on the OLED
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0,0);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(SET); OLED_printDec(CH224K_getVolt(), SPACE);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(CH224K_isGood() ? CMK : HGL);
|
||||
OLED_printVal(volt); OLED_printStr(mV);
|
||||
|
||||
OLED_setCursor(0,2);
|
||||
switch(seconds & 0x0C) {
|
||||
case 0x00: if(power > 65535) {
|
||||
OLED_printVal(power / 1000);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(Wt);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
OLED_printVal(power);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(mW);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 0x04: if(energy > 65535) {
|
||||
OLED_printVal(energy / 1000000);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(Wh);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
OLED_printVal(energy / 1000);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(mWh);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 0x08: if(charge > 65535) {
|
||||
OLED_printVal(charge / 1000000);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(Ah);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
OLED_printVal(charge / 1000);
|
||||
OLED_printStr(mAh);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 0x0C: OLED_printDec(seconds / 3600, 0); OLED_printChar(COLON);
|
||||
seconds %= 3600;
|
||||
OLED_printDec(seconds / 60 , 0); OLED_printChar(COLON);
|
||||
OLED_printDec(seconds % 60 , 0);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
OLED_printStr(SEP);
|
||||
OLED_printVal(curr); OLED_printStr(mA);
|
||||
_delay_ms(50);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
109
software/makefile
Executable file
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
# Project: USB PD Adapter
|
||||
# Author: Stefan Wagner
|
||||
# Year: 2022
|
||||
# URL: https://github.com/wagiminator
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Download AVR 8-bit Toolchain:
|
||||
# https://www.microchip.com/mplab/avr-support/avr-and-arm-toolchains-c-compilers
|
||||
# and extract to ./tools/avr-gcc
|
||||
# Type "make help" in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
# Input and Output File Names
|
||||
SKETCH = USB_PD_Adapter.ino
|
||||
TARGET = usb_pd_adapter
|
||||
|
||||
# Microcontroller Options
|
||||
DEVICE ?= attiny814
|
||||
CLOCK = 1000000
|
||||
FUSE0 = 0x00
|
||||
FUSE1 = 0x00
|
||||
FUSE2 = 0x01
|
||||
FUSE4 = 0x00
|
||||
FUSE5 = 0xC5
|
||||
FUSE6 = 0x04
|
||||
FUSE7 = 0x00
|
||||
FUSE8 = 0x00
|
||||
|
||||
# Programmer Options (serialupdi or jtag2updi)
|
||||
PROGRMR ?= serialupdi
|
||||
PORT ?= /dev/ttyUSB0
|
||||
|
||||
# Paths
|
||||
GCCPATH = ./tools/avr-gcc
|
||||
DFPPATH = ./tools/dfp
|
||||
PYMPATH = ./tools/pymcuprog
|
||||
ADCPATH = ./tools/avrdude
|
||||
|
||||
# Commands
|
||||
DFPINCL = -B $(DFPPATH)/gcc/dev/$(DEVICE)/ -I $(DFPPATH)/include/
|
||||
COMPILE = $(GCCPATH)/bin/avr-gcc $(DFPINCL) -flto -Wall -Os -mmcu=$(DEVICE) -DF_CPU=$(CLOCK)UL -x c++ $(SKETCH)
|
||||
PYPROG = python3 -u $(PYMPATH)/prog.py -t uart -u $(PORT) -b 230400 -d $(DEVICE)
|
||||
AVRDUDE = avrdude -C $(ADCPATH)/avrdude.conf -c jtag2updi -P $(PORT) -p $(DEVICE)
|
||||
CLEAN = rm -f *.lst *.obj *.cof *.list *.map *.eep.hex *.o *.s *.d
|
||||
|
||||
# Symbolic Targets
|
||||
help:
|
||||
@echo "Use the following commands:"
|
||||
@echo "make all compile and build $(TARGET).bin/.hex/.asm for $(DEVICE)"
|
||||
@echo "make hex compile and build $(TARGET).hex for $(DEVICE)"
|
||||
@echo "make asm compile and disassemble to $(TARGET).asm for $(DEVICE)"
|
||||
@echo "make bin compile and build $(TARGET).bin for $(DEVICE)"
|
||||
@echo "make upload compile and upload to $(DEVICE) using $(PROGRMR)"
|
||||
@echo "make fuses burn fuses of $(DEVICE) using $(PROGRMR) programmer"
|
||||
@echo "make install compile, upload and burn fuses for $(DEVICE)"
|
||||
@echo "make clean remove all build files"
|
||||
|
||||
all: buildbin buildhex buildasm removetemp size
|
||||
|
||||
bin: buildbin removetemp size
|
||||
|
||||
hex: buildbin buildhex removetemp size removebin
|
||||
|
||||
asm: buildbin buildasm removetemp size removebin
|
||||
|
||||
install: fuses upload
|
||||
|
||||
upload: hex
|
||||
@echo "Uploading to $(DEVICE) ..."
|
||||
ifeq ($(PROGRMR),serialupdi)
|
||||
@$(PYPROG) --fuses 2:$(FUSE2) 6:$(FUSE6) 8:$(FUSE8) -f $(TARGET).hex -a write
|
||||
else
|
||||
@$(AVRDUDE) -U fuse2:w:$(FUSE2):m -U fuse6:w:$(FUSE6):m -U fuse8:w:$(FUSE8):m -U flash:w:$(TARGET).hex:i
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
fuses:
|
||||
@echo "Burning fuses of $(DEVICE) ..."
|
||||
ifeq ($(PROGRMR),serialupdi)
|
||||
@$(PYPROG) --fuses 0:$(FUSE0) 1:$(FUSE1) 2:$(FUSE2) 4:$(FUSE4) 5:$(FUSE5) 6:$(FUSE6) 7:$(FUSE7) 8:$(FUSE8) -a erase
|
||||
else
|
||||
@$(AVRDUDE) -e -Ufuse0:w:$(FUSE0):m -Ufuse1:w:$(FUSE1):m -Ufuse2:w:$(FUSE2):m -Ufuse4:w:$(FUSE4):m -Ufuse5:w:$(FUSE5):m -Ufuse6:w:$(FUSE6):m -Ufuse7:w:$(FUSE7):m -Ufuse8:w:$(FUSE8):m
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
@echo "Cleaning all up ..."
|
||||
@$(CLEAN)
|
||||
@rm -f $(TARGET).bin $(TARGET).hex $(TARGET).asm
|
||||
|
||||
buildbin:
|
||||
@echo "Building $(TARGET).bin for $(DEVICE) @ $(CLOCK)Hz ..."
|
||||
@$(COMPILE) -o $(TARGET).bin
|
||||
|
||||
buildhex:
|
||||
@echo "Building $(TARGET).hex ..."
|
||||
@$(GCCPATH)/bin/avr-objcopy -O ihex -R .eeprom $(TARGET).bin $(TARGET).hex
|
||||
|
||||
buildasm:
|
||||
@echo "Disassembling to $(TARGET).asm ..."
|
||||
@$(GCCPATH)/bin/avr-objdump -d $(TARGET).bin > $(TARGET).asm
|
||||
|
||||
size:
|
||||
@echo "FLASH: $(shell $(GCCPATH)/bin/avr-size -d $(TARGET).bin | awk '/[0-9]/ {print $$1 + $$2}') bytes"
|
||||
@echo "SRAM: $(shell $(GCCPATH)/bin/avr-size -d $(TARGET).bin | awk '/[0-9]/ {print $$2 + $$3}') bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
removetemp:
|
||||
@echo "Removing temporary files ..."
|
||||
@$(CLEAN)
|
||||
|
||||
removebin:
|
||||
@echo "Removing $(TARGET).bin ..."
|
||||
@rm -f $(TARGET).bin
|
||||
4
software/tools/avr-gcc/download.txt
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Download AVR 8-bit Toolchain:
|
||||
https://www.microchip.com/mplab/avr-support/avr-and-arm-toolchains-c-compilers
|
||||
To do this, you have to register for free with Microchip on the site.
|
||||
Extract the sub-folders (avr, bin, include, ...) here.
|
||||
16284
software/tools/avrdude/avrdude.conf
Normal file
3
software/tools/avrdude/readme.txt
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Description: Modified avrdude config file to work with jtag2updi
|
||||
Source: https://github.com/ElTangas/jtag2updi
|
||||
License: MIT License
|
||||
BIN
software/tools/dfp/gcc/dev/attiny1604/avrxmega3/crtattiny1604.o
Normal file
BIN
software/tools/dfp/gcc/dev/attiny1604/avrxmega3/libattiny1604.a
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny1604 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny1604.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny1604}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
%{mpmem-wrap-around: --pmem-wrap-around=16k}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803C00
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 %<mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny1604__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny1604 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn1604
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
BIN
software/tools/dfp/gcc/dev/attiny1614/avrxmega3/crtattiny1614.o
Normal file
BIN
software/tools/dfp/gcc/dev/attiny1614/avrxmega3/libattiny1614.a
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny1614 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny1614.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny1614}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
%{mpmem-wrap-around: --pmem-wrap-around=16k}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803800
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 %<mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny1614__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny1614 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn1614
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny204 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP, short-calls)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny204.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny204}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803F80
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 -mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny204__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny204 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn204
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny214 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP, short-calls)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny214.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny214}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803F80
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 -mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny214__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny214 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn214
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny404 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP, short-calls)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny404.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny404}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803F00
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 -mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny404__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny404 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn404
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny414 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP, short-calls)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny414.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny414}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803F00
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 -mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny414__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny414 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn414
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny804 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP, short-calls)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny804.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny804}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
%{!mno-pmem-wrap-around: --pmem-wrap-around=8k}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803E00
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 -mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny804__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny804 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn804
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Auto-generated specs for AVR device attiny814 (core avrxmega3, 16-bit SP, short-calls)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Generated by : ./gcc/config/avr/gen-avr-mmcu-specs.c
|
||||
# Generated from : ./gcc/config/gcc.c
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/specs.h
|
||||
# ./gcc/config/avr/avrlibc.h
|
||||
# Used by : avr-gcc compiler driver
|
||||
# Used for : building command options for sub-processes
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Spec-Files.html>
|
||||
# for a documentation of spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# If you intend to use an existing device specs file as a starting point
|
||||
# for a new device spec file, make sure you are copying from a specs
|
||||
# file for a device from the same core architecture and SP width.
|
||||
# See <https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-5/changes.html> for a description
|
||||
# of how to use such own spec files.
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_startfile:
|
||||
crtattiny814.o%s
|
||||
|
||||
*avrlibc_devicelib:
|
||||
%{!nodevicelib:-lattiny814}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_n_flash:
|
||||
%{!mn-flash=*:-mn-flash=1}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*cc1_absdata:
|
||||
%{mabsdata}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_arch:
|
||||
-mmcu=avrxmega3
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--mlink-relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_rmw:
|
||||
%{mrmw}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_gccisr:
|
||||
%{!mno-gas-isr-prologues: -mgcc-isr}
|
||||
|
||||
*asm_errata_skip:
|
||||
%{!mskip-bug: -mno-skip-bug}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_pmem_wrap:
|
||||
%{!mno-pmem-wrap-around: --pmem-wrap-around=8k}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_relax:
|
||||
%{mrelax:--relax}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_arch:
|
||||
%{mmcu=*:-m%*}
|
||||
|
||||
*link_data_start:
|
||||
-Tdata 0x803E00
|
||||
|
||||
*link_text_start:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*self_spec:
|
||||
%<mmcu=* -mmcu=avrxmega3 -mshort-calls %<msp8
|
||||
|
||||
# AVR-LibC's avr/io.h uses the device specifying macro to determine
|
||||
# the name of the device header. For example, -mmcu=atmega8a triggers
|
||||
# the definition of __AVR_ATmega8A__ and avr/io.h includes the device
|
||||
# header 'iom8a.h' by means of:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
# #elif defined (__AVR_ATmega8A__)
|
||||
# # include <avr/iom8a.h>
|
||||
# #elif ...
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If no device macro is defined, AVR-LibC uses __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as fallback to determine the name of the device header as
|
||||
#
|
||||
# "avr/io" + __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__ + ".h"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If you provide your own specs file for a device not yet known to
|
||||
# AVR-LibC, you can now define the hook macro __AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__
|
||||
# as needed so that
|
||||
#
|
||||
# #include <avr/io.h>
|
||||
#
|
||||
# will include the desired device header. For ATmega8A the supplement
|
||||
# to *cpp would read
|
||||
#
|
||||
# -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=m8a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*cpp:
|
||||
-D__AVR_ATtiny814__ -D__AVR_DEVICE_NAME__=attiny814 -D__AVR_DEV_LIB_NAME__=tn814
|
||||
|
||||
%rename link old_link
|
||||
|
||||
*link:
|
||||
%(old_link)--defsym=__RODATA_PM_OFFSET__=0x8000
|
||||
|
||||
# End of file
|
||||
4667
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn1604.h
Normal file
5536
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn1614.h
Normal file
4658
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn204.h
Normal file
5296
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn214.h
Normal file
4658
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn404.h
Normal file
5296
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn414.h
Normal file
4667
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn804.h
Normal file
5278
software/tools/dfp/include/avr/iotn814.h
Normal file
64
software/tools/dfp/include/component-version.h
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* \file
|
||||
*
|
||||
* \brief Component version header file
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2021 Atmel Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Microchip Technology Inc.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* \license_start
|
||||
*
|
||||
* \page License
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
*
|
||||
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
* limitations under the License.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* \license_stop
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _COMPONENT_VERSION_H_INCLUDED
|
||||
#define _COMPONENT_VERSION_H_INCLUDED
|
||||
|
||||
#define COMPONENT_VERSION_MAJOR 2
|
||||
#define COMPONENT_VERSION_MINOR 7
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The COMPONENT_VERSION define is composed of the major and the minor version number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The last four digits of the COMPONENT_VERSION is the minor version with leading zeros.
|
||||
// The rest of the COMPONENT_VERSION is the major version.
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define COMPONENT_VERSION 20007
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The build number does not refer to the component, but to the build number
|
||||
// of the device pack that provides the component.
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define BUILD_NUMBER 128
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The COMPONENT_VERSION_STRING is a string (enclosed in ") that can be used for logging or embedding.
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define COMPONENT_VERSION_STRING "2.7"
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The COMPONENT_DATE_STRING contains a timestamp of when the pack was generated.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The COMPONENT_DATE_STRING is written out using the following strftime pattern.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
#define COMPONENT_DATE_STRING "2021-07-13 10:42:36"
|
||||
|
||||
#endif/* #ifndef _COMPONENT_VERSION_H_INCLUDED */
|
||||
|
||||
17
software/tools/dfp/readme.txt
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
Description: Atmel ATtiny Series Device Support (1.10.348)
|
||||
|
||||
Source: http://packs.download.atmel.com/
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2020 Microchip Technology Inc.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the Licence at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
608
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/appdirs.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,608 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2005-2010 ActiveState Software Inc.
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2013 Eddy Petrișor
|
||||
|
||||
"""Utilities for determining application-specific dirs.
|
||||
|
||||
See <http://github.com/ActiveState/appdirs> for details and usage.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Dev Notes:
|
||||
# - MSDN on where to store app data files:
|
||||
# http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;310294#XSLTH3194121123120121120120
|
||||
# - Mac OS X: http://developer.apple.com/documentation/MacOSX/Conceptual/BPFileSystem/index.html
|
||||
# - XDG spec for Un*x: http://standards.freedesktop.org/basedir-spec/basedir-spec-latest.html
|
||||
|
||||
__version__ = "1.4.4"
|
||||
__version_info__ = tuple(int(segment) for segment in __version__.split("."))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
PY3 = sys.version_info[0] == 3
|
||||
|
||||
if PY3:
|
||||
unicode = str
|
||||
|
||||
if sys.platform.startswith('java'):
|
||||
import platform
|
||||
os_name = platform.java_ver()[3][0]
|
||||
if os_name.startswith('Windows'): # "Windows XP", "Windows 7", etc.
|
||||
system = 'win32'
|
||||
elif os_name.startswith('Mac'): # "Mac OS X", etc.
|
||||
system = 'darwin'
|
||||
else: # "Linux", "SunOS", "FreeBSD", etc.
|
||||
# Setting this to "linux2" is not ideal, but only Windows or Mac
|
||||
# are actually checked for and the rest of the module expects
|
||||
# *sys.platform* style strings.
|
||||
system = 'linux2'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
system = sys.platform
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def user_data_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, roaming=False):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-specific data dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"roaming" (boolean, default False) can be set True to use the Windows
|
||||
roaming appdata directory. That means that for users on a Windows
|
||||
network setup for roaming profiles, this user data will be
|
||||
sync'd on login. See
|
||||
<http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766489(WS.10).aspx>
|
||||
for a discussion of issues.
|
||||
|
||||
Typical user data directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: ~/Library/Application Support/<AppName>
|
||||
Unix: ~/.local/share/<AppName> # or in $XDG_DATA_HOME, if defined
|
||||
Win XP (not roaming): C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
Win XP (roaming): C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
Win 7 (not roaming): C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
Win 7 (roaming): C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
|
||||
For Unix, we follow the XDG spec and support $XDG_DATA_HOME.
|
||||
That means, by default "~/.local/share/<AppName>".
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system == "win32":
|
||||
if appauthor is None:
|
||||
appauthor = appname
|
||||
const = roaming and "CSIDL_APPDATA" or "CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA"
|
||||
path = os.path.normpath(_get_win_folder(const))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
if appauthor is not False:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appauthor, appname)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
elif system == 'darwin':
|
||||
path = os.path.expanduser('~/Library/Application Support/')
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.getenv('XDG_DATA_HOME', os.path.expanduser("~/.local/share"))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def site_data_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, multipath=False):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-shared data dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"multipath" is an optional parameter only applicable to *nix
|
||||
which indicates that the entire list of data dirs should be
|
||||
returned. By default, the first item from XDG_DATA_DIRS is
|
||||
returned, or '/usr/local/share/<AppName>',
|
||||
if XDG_DATA_DIRS is not set
|
||||
|
||||
Typical site data directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: /Library/Application Support/<AppName>
|
||||
Unix: /usr/local/share/<AppName> or /usr/share/<AppName>
|
||||
Win XP: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>
|
||||
Vista: (Fail! "C:\ProgramData" is a hidden *system* directory on Vista.)
|
||||
Win 7: C:\ProgramData\<AppAuthor>\<AppName> # Hidden, but writeable on Win 7.
|
||||
|
||||
For Unix, this is using the $XDG_DATA_DIRS[0] default.
|
||||
|
||||
WARNING: Do not use this on Windows. See the Vista-Fail note above for why.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system == "win32":
|
||||
if appauthor is None:
|
||||
appauthor = appname
|
||||
path = os.path.normpath(_get_win_folder("CSIDL_COMMON_APPDATA"))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
if appauthor is not False:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appauthor, appname)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
elif system == 'darwin':
|
||||
path = os.path.expanduser('/Library/Application Support')
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# XDG default for $XDG_DATA_DIRS
|
||||
# only first, if multipath is False
|
||||
path = os.getenv('XDG_DATA_DIRS',
|
||||
os.pathsep.join(['/usr/local/share', '/usr/share']))
|
||||
pathlist = [os.path.expanduser(x.rstrip(os.sep)) for x in path.split(os.pathsep)]
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
if version:
|
||||
appname = os.path.join(appname, version)
|
||||
pathlist = [os.sep.join([x, appname]) for x in pathlist]
|
||||
|
||||
if multipath:
|
||||
path = os.pathsep.join(pathlist)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = pathlist[0]
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def user_config_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, roaming=False):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-specific config dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"roaming" (boolean, default False) can be set True to use the Windows
|
||||
roaming appdata directory. That means that for users on a Windows
|
||||
network setup for roaming profiles, this user data will be
|
||||
sync'd on login. See
|
||||
<http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766489(WS.10).aspx>
|
||||
for a discussion of issues.
|
||||
|
||||
Typical user config directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: same as user_data_dir
|
||||
Unix: ~/.config/<AppName> # or in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME, if defined
|
||||
Win *: same as user_data_dir
|
||||
|
||||
For Unix, we follow the XDG spec and support $XDG_CONFIG_HOME.
|
||||
That means, by default "~/.config/<AppName>".
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system in ["win32", "darwin"]:
|
||||
path = user_data_dir(appname, appauthor, None, roaming)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.getenv('XDG_CONFIG_HOME', os.path.expanduser("~/.config"))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def site_config_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, multipath=False):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-shared data dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"multipath" is an optional parameter only applicable to *nix
|
||||
which indicates that the entire list of config dirs should be
|
||||
returned. By default, the first item from XDG_CONFIG_DIRS is
|
||||
returned, or '/etc/xdg/<AppName>', if XDG_CONFIG_DIRS is not set
|
||||
|
||||
Typical site config directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: same as site_data_dir
|
||||
Unix: /etc/xdg/<AppName> or $XDG_CONFIG_DIRS[i]/<AppName> for each value in
|
||||
$XDG_CONFIG_DIRS
|
||||
Win *: same as site_data_dir
|
||||
Vista: (Fail! "C:\ProgramData" is a hidden *system* directory on Vista.)
|
||||
|
||||
For Unix, this is using the $XDG_CONFIG_DIRS[0] default, if multipath=False
|
||||
|
||||
WARNING: Do not use this on Windows. See the Vista-Fail note above for why.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system in ["win32", "darwin"]:
|
||||
path = site_data_dir(appname, appauthor)
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# XDG default for $XDG_CONFIG_DIRS
|
||||
# only first, if multipath is False
|
||||
path = os.getenv('XDG_CONFIG_DIRS', '/etc/xdg')
|
||||
pathlist = [os.path.expanduser(x.rstrip(os.sep)) for x in path.split(os.pathsep)]
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
if version:
|
||||
appname = os.path.join(appname, version)
|
||||
pathlist = [os.sep.join([x, appname]) for x in pathlist]
|
||||
|
||||
if multipath:
|
||||
path = os.pathsep.join(pathlist)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = pathlist[0]
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def user_cache_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, opinion=True):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-specific cache dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"opinion" (boolean) can be False to disable the appending of
|
||||
"Cache" to the base app data dir for Windows. See
|
||||
discussion below.
|
||||
|
||||
Typical user cache directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: ~/Library/Caches/<AppName>
|
||||
Unix: ~/.cache/<AppName> (XDG default)
|
||||
Win XP: C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Cache
|
||||
Vista: C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Cache
|
||||
|
||||
On Windows the only suggestion in the MSDN docs is that local settings go in
|
||||
the `CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA` directory. This is identical to the non-roaming
|
||||
app data dir (the default returned by `user_data_dir` above). Apps typically
|
||||
put cache data somewhere *under* the given dir here. Some examples:
|
||||
...\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\<ProfileName>\Cache
|
||||
...\Acme\SuperApp\Cache\1.0
|
||||
OPINION: This function appends "Cache" to the `CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA` value.
|
||||
This can be disabled with the `opinion=False` option.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system == "win32":
|
||||
if appauthor is None:
|
||||
appauthor = appname
|
||||
path = os.path.normpath(_get_win_folder("CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA"))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
if appauthor is not False:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appauthor, appname)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
if opinion:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, "Cache")
|
||||
elif system == 'darwin':
|
||||
path = os.path.expanduser('~/Library/Caches')
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.getenv('XDG_CACHE_HOME', os.path.expanduser('~/.cache'))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def user_state_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, roaming=False):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-specific state dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"roaming" (boolean, default False) can be set True to use the Windows
|
||||
roaming appdata directory. That means that for users on a Windows
|
||||
network setup for roaming profiles, this user data will be
|
||||
sync'd on login. See
|
||||
<http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766489(WS.10).aspx>
|
||||
for a discussion of issues.
|
||||
|
||||
Typical user state directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: same as user_data_dir
|
||||
Unix: ~/.local/state/<AppName> # or in $XDG_STATE_HOME, if defined
|
||||
Win *: same as user_data_dir
|
||||
|
||||
For Unix, we follow this Debian proposal <https://wiki.debian.org/XDGBaseDirectorySpecification#state>
|
||||
to extend the XDG spec and support $XDG_STATE_HOME.
|
||||
|
||||
That means, by default "~/.local/state/<AppName>".
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system in ["win32", "darwin"]:
|
||||
path = user_data_dir(appname, appauthor, None, roaming)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = os.getenv('XDG_STATE_HOME', os.path.expanduser("~/.local/state"))
|
||||
if appname:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, appname)
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def user_log_dir(appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None, opinion=True):
|
||||
r"""Return full path to the user-specific log dir for this application.
|
||||
|
||||
"appname" is the name of application.
|
||||
If None, just the system directory is returned.
|
||||
"appauthor" (only used on Windows) is the name of the
|
||||
appauthor or distributing body for this application. Typically
|
||||
it is the owning company name. This falls back to appname. You may
|
||||
pass False to disable it.
|
||||
"version" is an optional version path element to append to the
|
||||
path. You might want to use this if you want multiple versions
|
||||
of your app to be able to run independently. If used, this
|
||||
would typically be "<major>.<minor>".
|
||||
Only applied when appname is present.
|
||||
"opinion" (boolean) can be False to disable the appending of
|
||||
"Logs" to the base app data dir for Windows, and "log" to the
|
||||
base cache dir for Unix. See discussion below.
|
||||
|
||||
Typical user log directories are:
|
||||
Mac OS X: ~/Library/Logs/<AppName>
|
||||
Unix: ~/.cache/<AppName>/log # or under $XDG_CACHE_HOME if defined
|
||||
Win XP: C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Logs
|
||||
Vista: C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\<AppAuthor>\<AppName>\Logs
|
||||
|
||||
On Windows the only suggestion in the MSDN docs is that local settings
|
||||
go in the `CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA` directory. (Note: I'm interested in
|
||||
examples of what some windows apps use for a logs dir.)
|
||||
|
||||
OPINION: This function appends "Logs" to the `CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA`
|
||||
value for Windows and appends "log" to the user cache dir for Unix.
|
||||
This can be disabled with the `opinion=False` option.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if system == "darwin":
|
||||
path = os.path.join(
|
||||
os.path.expanduser('~/Library/Logs'),
|
||||
appname)
|
||||
elif system == "win32":
|
||||
path = user_data_dir(appname, appauthor, version)
|
||||
version = False
|
||||
if opinion:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, "Logs")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
path = user_cache_dir(appname, appauthor, version)
|
||||
version = False
|
||||
if opinion:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, "log")
|
||||
if appname and version:
|
||||
path = os.path.join(path, version)
|
||||
return path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AppDirs(object):
|
||||
"""Convenience wrapper for getting application dirs."""
|
||||
def __init__(self, appname=None, appauthor=None, version=None,
|
||||
roaming=False, multipath=False):
|
||||
self.appname = appname
|
||||
self.appauthor = appauthor
|
||||
self.version = version
|
||||
self.roaming = roaming
|
||||
self.multipath = multipath
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def user_data_dir(self):
|
||||
return user_data_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version, roaming=self.roaming)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def site_data_dir(self):
|
||||
return site_data_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version, multipath=self.multipath)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def user_config_dir(self):
|
||||
return user_config_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version, roaming=self.roaming)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def site_config_dir(self):
|
||||
return site_config_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version, multipath=self.multipath)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def user_cache_dir(self):
|
||||
return user_cache_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def user_state_dir(self):
|
||||
return user_state_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def user_log_dir(self):
|
||||
return user_log_dir(self.appname, self.appauthor,
|
||||
version=self.version)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#---- internal support stuff
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_win_folder_from_registry(csidl_name):
|
||||
"""This is a fallback technique at best. I'm not sure if using the
|
||||
registry for this guarantees us the correct answer for all CSIDL_*
|
||||
names.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if PY3:
|
||||
import winreg as _winreg
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import _winreg
|
||||
|
||||
shell_folder_name = {
|
||||
"CSIDL_APPDATA": "AppData",
|
||||
"CSIDL_COMMON_APPDATA": "Common AppData",
|
||||
"CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA": "Local AppData",
|
||||
}[csidl_name]
|
||||
|
||||
key = _winreg.OpenKey(
|
||||
_winreg.HKEY_CURRENT_USER,
|
||||
r"Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell Folders"
|
||||
)
|
||||
dir, type = _winreg.QueryValueEx(key, shell_folder_name)
|
||||
return dir
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_win_folder_with_pywin32(csidl_name):
|
||||
from win32com.shell import shellcon, shell
|
||||
dir = shell.SHGetFolderPath(0, getattr(shellcon, csidl_name), 0, 0)
|
||||
# Try to make this a unicode path because SHGetFolderPath does
|
||||
# not return unicode strings when there is unicode data in the
|
||||
# path.
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dir = unicode(dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# Downgrade to short path name if have highbit chars. See
|
||||
# <http://bugs.activestate.com/show_bug.cgi?id=85099>.
|
||||
has_high_char = False
|
||||
for c in dir:
|
||||
if ord(c) > 255:
|
||||
has_high_char = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
if has_high_char:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import win32api
|
||||
dir = win32api.GetShortPathName(dir)
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
except UnicodeError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
return dir
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_win_folder_with_ctypes(csidl_name):
|
||||
import ctypes
|
||||
|
||||
csidl_const = {
|
||||
"CSIDL_APPDATA": 26,
|
||||
"CSIDL_COMMON_APPDATA": 35,
|
||||
"CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA": 28,
|
||||
}[csidl_name]
|
||||
|
||||
buf = ctypes.create_unicode_buffer(1024)
|
||||
ctypes.windll.shell32.SHGetFolderPathW(None, csidl_const, None, 0, buf)
|
||||
|
||||
# Downgrade to short path name if have highbit chars. See
|
||||
# <http://bugs.activestate.com/show_bug.cgi?id=85099>.
|
||||
has_high_char = False
|
||||
for c in buf:
|
||||
if ord(c) > 255:
|
||||
has_high_char = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
if has_high_char:
|
||||
buf2 = ctypes.create_unicode_buffer(1024)
|
||||
if ctypes.windll.kernel32.GetShortPathNameW(buf.value, buf2, 1024):
|
||||
buf = buf2
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.value
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_win_folder_with_jna(csidl_name):
|
||||
import array
|
||||
from com.sun import jna
|
||||
from com.sun.jna.platform import win32
|
||||
|
||||
buf_size = win32.WinDef.MAX_PATH * 2
|
||||
buf = array.zeros('c', buf_size)
|
||||
shell = win32.Shell32.INSTANCE
|
||||
shell.SHGetFolderPath(None, getattr(win32.ShlObj, csidl_name), None, win32.ShlObj.SHGFP_TYPE_CURRENT, buf)
|
||||
dir = jna.Native.toString(buf.tostring()).rstrip("\0")
|
||||
|
||||
# Downgrade to short path name if have highbit chars. See
|
||||
# <http://bugs.activestate.com/show_bug.cgi?id=85099>.
|
||||
has_high_char = False
|
||||
for c in dir:
|
||||
if ord(c) > 255:
|
||||
has_high_char = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
if has_high_char:
|
||||
buf = array.zeros('c', buf_size)
|
||||
kernel = win32.Kernel32.INSTANCE
|
||||
if kernel.GetShortPathName(dir, buf, buf_size):
|
||||
dir = jna.Native.toString(buf.tostring()).rstrip("\0")
|
||||
|
||||
return dir
|
||||
|
||||
if system == "win32":
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import win32com.shell
|
||||
_get_win_folder = _get_win_folder_with_pywin32
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from ctypes import windll
|
||||
_get_win_folder = _get_win_folder_with_ctypes
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import com.sun.jna
|
||||
_get_win_folder = _get_win_folder_with_jna
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
_get_win_folder = _get_win_folder_from_registry
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#---- self test code
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
appname = "MyApp"
|
||||
appauthor = "MyCompany"
|
||||
|
||||
props = ("user_data_dir",
|
||||
"user_config_dir",
|
||||
"user_cache_dir",
|
||||
"user_state_dir",
|
||||
"user_log_dir",
|
||||
"site_data_dir",
|
||||
"site_config_dir")
|
||||
|
||||
print("-- app dirs %s --" % __version__)
|
||||
|
||||
print("-- app dirs (with optional 'version')")
|
||||
dirs = AppDirs(appname, appauthor, version="1.0")
|
||||
for prop in props:
|
||||
print("%s: %s" % (prop, getattr(dirs, prop)))
|
||||
|
||||
print("\n-- app dirs (without optional 'version')")
|
||||
dirs = AppDirs(appname, appauthor)
|
||||
for prop in props:
|
||||
print("%s: %s" % (prop, getattr(dirs, prop)))
|
||||
|
||||
print("\n-- app dirs (without optional 'appauthor')")
|
||||
dirs = AppDirs(appname)
|
||||
for prop in props:
|
||||
print("%s: %s" % (prop, getattr(dirs, prop)))
|
||||
|
||||
print("\n-- app dirs (with disabled 'appauthor')")
|
||||
dirs = AppDirs(appname, appauthor=False)
|
||||
for prop in props:
|
||||
print("%s: %s" % (prop, getattr(dirs, prop)))
|
||||
1372
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/intelhex/__init__.py
Normal file
160
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/intelhex/compat.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,160 @@
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2011, Bernhard Leiner
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2013-2018 Alexander Belchenko
|
||||
# All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Redistribution and use in source and binary forms,
|
||||
# with or without modification, are permitted provided
|
||||
# that the following conditions are met:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# * Redistributions of source code must retain
|
||||
# the above copyright notice, this list of conditions
|
||||
# and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
# * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce
|
||||
# the above copyright notice, this list of conditions
|
||||
# and the following disclaimer in the documentation
|
||||
# and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
|
||||
# * Neither the name of the author nor the names
|
||||
# of its contributors may be used to endorse
|
||||
# or promote products derived from this software
|
||||
# without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
# "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING,
|
||||
# BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
|
||||
# AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
|
||||
# IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
|
||||
# FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY,
|
||||
# OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
|
||||
# PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA,
|
||||
# OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED
|
||||
# AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT,
|
||||
# STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
|
||||
# ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE,
|
||||
# EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
|
||||
'''Compatibility functions for python 2 and 3.
|
||||
|
||||
@author Bernhard Leiner (bleiner AT gmail com)
|
||||
@author Alexander Belchenko (alexander belchenko AT gmail com)
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
__docformat__ = "javadoc"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import sys, array
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
|
||||
# Python 3
|
||||
Python = 3
|
||||
|
||||
def asbytes(s):
|
||||
if isinstance(s, bytes):
|
||||
return s
|
||||
return s.encode('latin1')
|
||||
def asstr(s):
|
||||
if isinstance(s, str):
|
||||
return s
|
||||
return s.decode('latin1')
|
||||
|
||||
# for python >= 3.2 use 'tobytes', otherwise 'tostring'
|
||||
array_tobytes = array.array.tobytes if sys.version_info[1] >= 2 else array.array.tostring
|
||||
|
||||
IntTypes = (int,)
|
||||
StrType = str
|
||||
UnicodeType = str
|
||||
|
||||
range_g = range # range generator
|
||||
def range_l(*args): # range list
|
||||
return list(range(*args))
|
||||
|
||||
def dict_keys(dikt): # dict keys list
|
||||
return list(dikt.keys())
|
||||
def dict_keys_g(dikt): # dict keys generator
|
||||
return dikt.keys()
|
||||
def dict_items_g(dikt): # dict items generator
|
||||
return dikt.items()
|
||||
|
||||
from io import StringIO, BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
def get_binary_stdout():
|
||||
return sys.stdout.buffer
|
||||
|
||||
def get_binary_stdin():
|
||||
return sys.stdin.buffer
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Python 2
|
||||
Python = 2
|
||||
|
||||
asbytes = str
|
||||
asstr = str
|
||||
|
||||
array_tobytes = array.array.tostring
|
||||
|
||||
IntTypes = (int, long)
|
||||
StrType = basestring
|
||||
UnicodeType = unicode
|
||||
|
||||
#range_g = xrange # range generator
|
||||
def range_g(*args):
|
||||
# we want to use xrange here but on python 2 it does not work with long ints
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return xrange(*args)
|
||||
except OverflowError:
|
||||
start = 0
|
||||
stop = 0
|
||||
step = 1
|
||||
n = len(args)
|
||||
if n == 1:
|
||||
stop = args[0]
|
||||
elif n == 2:
|
||||
start, stop = args
|
||||
elif n == 3:
|
||||
start, stop, step = args
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise TypeError('wrong number of arguments in range_g call!')
|
||||
if step == 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError('step cannot be zero')
|
||||
if step > 0:
|
||||
def up(start, stop, step):
|
||||
while start < stop:
|
||||
yield start
|
||||
start += step
|
||||
return up(start, stop, step)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
def down(start, stop, step):
|
||||
while start > stop:
|
||||
yield start
|
||||
start += step
|
||||
return down(start, stop, step)
|
||||
|
||||
range_l = range # range list
|
||||
|
||||
def dict_keys(dikt): # dict keys list
|
||||
return dikt.keys()
|
||||
def dict_keys_g(dikt): # dict keys generator
|
||||
return dikt.keys()
|
||||
def dict_items_g(dikt): # dict items generator
|
||||
return dikt.items()
|
||||
|
||||
from cStringIO import StringIO
|
||||
BytesIO = StringIO
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
def _force_stream_binary(stream):
|
||||
"""Force binary mode for stream on Windows."""
|
||||
if os.name == 'nt':
|
||||
f_fileno = getattr(stream, 'fileno', None)
|
||||
if f_fileno:
|
||||
fileno = f_fileno()
|
||||
if fileno >= 0:
|
||||
import msvcrt
|
||||
msvcrt.setmode(fileno, os.O_BINARY)
|
||||
return stream
|
||||
|
||||
def get_binary_stdout():
|
||||
return _force_stream_binary(sys.stdout)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_binary_stdin():
|
||||
return _force_stream_binary(sys.stdin)
|
||||
64
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/intelhex/getsizeof.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
# Recursive version sys.getsizeof(). Extendable with custom handlers.
|
||||
# Code from http://code.activestate.com/recipes/577504/
|
||||
# Created by Raymond Hettinger on Fri, 17 Dec 2010 (MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from itertools import chain
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from reprlib import repr
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def total_size(o, handlers={}, verbose=False):
|
||||
""" Returns the approximate memory footprint an object and all of its contents.
|
||||
|
||||
Automatically finds the contents of the following builtin containers and
|
||||
their subclasses: tuple, list, deque, dict, set and frozenset.
|
||||
To search other containers, add handlers to iterate over their contents:
|
||||
|
||||
handlers = {SomeContainerClass: iter,
|
||||
OtherContainerClass: OtherContainerClass.get_elements}
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
dict_handler = lambda d: chain.from_iterable(d.items())
|
||||
all_handlers = {tuple: iter,
|
||||
list: iter,
|
||||
deque: iter,
|
||||
dict: dict_handler,
|
||||
set: iter,
|
||||
frozenset: iter,
|
||||
}
|
||||
all_handlers.update(handlers) # user handlers take precedence
|
||||
seen = set() # track which object id's have already been seen
|
||||
default_size = sys.getsizeof(0) # estimate sizeof object without __sizeof__
|
||||
|
||||
def sizeof(o):
|
||||
if id(o) in seen: # do not double count the same object
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
seen.add(id(o))
|
||||
s = sys.getsizeof(o, default_size)
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(s, type(o), repr(o))#, file=stderr)
|
||||
|
||||
for typ, handler in all_handlers.items():
|
||||
if isinstance(o, typ):
|
||||
s += sum(map(sizeof, handler(o)))
|
||||
break
|
||||
return s
|
||||
|
||||
return sizeof(o)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### Example call #####
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
#d = dict(a=1, b=2, c=3, d=[4,5,6,7], e='a string of chars')
|
||||
print("dict 3 elements")
|
||||
d = {0:0xFF, 1:0xEE, 2:0xCC}
|
||||
print(total_size(d, verbose=True))
|
||||
|
||||
#print("array 3 elements")
|
||||
#import array
|
||||
#print(total_size(array.array('B', b'\x01\x02\x03')))
|
||||
46
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pyedbglib/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Python EDBG protocol communication library
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
pyedbglib is a low-level protocol library for communicating with
|
||||
Microchip CMSIS-DAP based debuggers.
|
||||
|
||||
pyedbglib uses HIDAPI package with a USB-level driver such as libusb.
|
||||
|
||||
The protocol library has no application usage on its own, but provides
|
||||
USB-protocol-level tool drivers to applications such as pymcuprog.
|
||||
In general a two-stage stack implementation is required for using pyedbglib:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create transport HID layer
|
||||
2. Create protocol implementation using this transport layer
|
||||
|
||||
All protocols implemented in the library generally take the transport layer
|
||||
as a parameter to their constructors.
|
||||
|
||||
To use pyedbglib as a library for applications, the following usage patterns
|
||||
can be used:
|
||||
|
||||
Import and instantiate transport object:
|
||||
|
||||
>>> from pyedbglib.hidtransport.hidtransportfactory import hid_transport
|
||||
>>> transport = hid_transport()
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to any nEDBG tool. Serial number and product are optional, but must
|
||||
be provided if more than one matching unit is connected:
|
||||
|
||||
>>> status = transport.connect(serial_number="", product="nedbg")
|
||||
|
||||
Example of application using housekeeping protocol to read out the target voltage:
|
||||
|
||||
>>> from pyedbglib.protocols.housekeepingprotocol import Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol
|
||||
>>> housekeeper = Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol(transport)
|
||||
>>> housekeeper.start_session()
|
||||
>>> voltage = housekeeper.get_le16(Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_ANALOG,
|
||||
Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol.HOUSEKEEPING_ANALOG_VTREF)
|
||||
>>> voltage = voltage / 1000.0
|
||||
>>> housekeeper.end_session()
|
||||
>>> print ("Target is running at {0:.02f}V".format(voltage))
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
logging.getLogger(__name__).addHandler(logging.NullHandler())
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
|
||||
"""Base class for all HID transport mechanisms."""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
from . import toolinfo
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HidTool(object):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Holds transport and DAP properties of a CMSIS-DAP debugger.
|
||||
|
||||
Used to select the debugger to use if multiple debuggers are connected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# pylint: disable=too-many-instance-attributes, too-many-arguments
|
||||
# These are primary keys used to identify the debugger.
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, vendor_id, product_id, serial_number, product_string="", manufacturer_string=""):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.interface_number = -1
|
||||
self.vendor_id = vendor_id
|
||||
self.product_id = product_id
|
||||
self.serial_number = serial_number
|
||||
self.product_string = product_string
|
||||
self.manufacturer_string = manufacturer_string
|
||||
self.firmware_version = ""
|
||||
self.device_vendor_id = ""
|
||||
self.device_name = ""
|
||||
self.packet_size = 64
|
||||
|
||||
def set_packet_size(self, packet_size):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sets the packet size
|
||||
|
||||
:param packet_size: bytes per packet
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.packet_size = packet_size
|
||||
|
||||
def set_product_string(self, product_string):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sets the product string
|
||||
|
||||
:param product_string: product name string
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.product_string = product_string
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HidTransportBase(object):
|
||||
"""Base class for HID transports"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.devices = []
|
||||
self.device = None
|
||||
self.detect_devices()
|
||||
self.connected = False
|
||||
|
||||
def __del__(self):
|
||||
# Make sure we always disconnect the HID connection
|
||||
self.disconnect()
|
||||
|
||||
def detect_devices(self):
|
||||
"""Raise error as this method needs to be overridden."""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("method needs to be defined by sub-class")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_matching_tools(self, serial_number_substring='', product=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a list of tools matching the given serial_number_substring and product.
|
||||
|
||||
:param serial_number_substring: can be an empty string or a subset of a serial number. Not case sensitive
|
||||
This function will do matching of the last part of the devices serial numbers to
|
||||
the serial_number_substring. Examples:
|
||||
'123' will match "MCHP3252000000043123" but not "MCP32520001230000000"
|
||||
'' will match any serial number
|
||||
:param product: product type to connect to. If None any tool matching the serial_number_substring
|
||||
will be returned
|
||||
:return: List of matching tools
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Support systems which use None as the standard for a unspecified USB serial
|
||||
if serial_number_substring is None:
|
||||
serial_number_substring = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Making serial_number_substring case insensitive
|
||||
serial_number_substring = serial_number_substring.lower()
|
||||
|
||||
# Support tool shortnames
|
||||
toolname_in_product_string = toolinfo.tool_shortname_to_product_string_name(product)
|
||||
if toolname_in_product_string is not None:
|
||||
# Making product name case insensitive
|
||||
toolname_in_product_string = toolname_in_product_string.lower()
|
||||
|
||||
matching_devices = []
|
||||
for device in self.devices:
|
||||
if toolname_in_product_string is None or device.product_string.lower().startswith(
|
||||
toolname_in_product_string):
|
||||
if device.serial_number.lower().endswith(serial_number_substring):
|
||||
matching_devices.append(device)
|
||||
|
||||
return matching_devices
|
||||
|
||||
def connect(self, serial_number=None, product=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Makes a HID connection to a debugger
|
||||
|
||||
:param serial_number: instance serial number to connect to
|
||||
:param product: product type to connect to
|
||||
:return: True if successfully connected to a tool, False if not
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.connected:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
device_count = len(self.devices)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("{:d} devices available".format(device_count))
|
||||
if device_count == 0:
|
||||
self.logger.error("No CMSIS-DAP devices found.")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
matching_devices = self.get_matching_tools(serial_number_substring=serial_number, product=product)
|
||||
number_of_matching_devices = len(matching_devices)
|
||||
|
||||
# Did we find exactly 1 tool?
|
||||
if number_of_matching_devices != 1:
|
||||
log_str = "Found {:d} daps matching the filter serial = \"{}\" and product = \"{}\""
|
||||
self.logger.debug(log_str.format(number_of_matching_devices, serial_number, product))
|
||||
if number_of_matching_devices > 1:
|
||||
self.logger.error("Too many products found. Please specify one of:")
|
||||
for device in self.devices:
|
||||
self.logger.error(" > {:s} {:s}".format(device.product_string,
|
||||
device.serial_number))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# Everything is peachy, connect to the tool
|
||||
self.device = matching_devices[0]
|
||||
self.hid_connect(self.device)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Connected OK")
|
||||
self.connected = True
|
||||
packet_size = toolinfo.get_default_report_size(self.device.product_id)
|
||||
self.device.set_packet_size(packet_size)
|
||||
self.hid_info()
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def disconnect(self):
|
||||
"""Release the HID connection"""
|
||||
if self.connected:
|
||||
self.hid_disconnect()
|
||||
self.connected = False
|
||||
|
||||
def hid_connect(self, device):
|
||||
"""Raise error as this method needs to be overridden."""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("method needs to be defined by sub-class")
|
||||
|
||||
def hid_info(self):
|
||||
"""Raise error as this method needs to be overridden."""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("method needs to be defined by sub-class")
|
||||
|
||||
def hid_disconnect(self):
|
||||
"""Raise error as this method needs to be overridden."""
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("method needs to be defined by sub-class")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_report_size(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the packet size in bytes
|
||||
|
||||
:return: bytes per packet/report
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.device.packet_size
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Factory for HID transport connections.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently supports only Cython/HIDAPI
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import platform
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
from ..pyedbglib_errors import PyedbglibNotSupportedError
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def hid_transport(library="hidapi"):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Dispatch a transport layer for the OS in question
|
||||
|
||||
The transport layer is typically used to connect to a tool and then it is passed in as a parameter when creating
|
||||
protocol objects. An example where the transport layer is used to create an instance of the housekeepingprotocol
|
||||
for communication with the nEDBG debugger::
|
||||
|
||||
from pyedbglib.hidtransport.hidtransportfactory import hid_transport
|
||||
transport = hid_transport()
|
||||
connect_status = False
|
||||
try:
|
||||
connect_status = transport.connect(serial_number='', product='nedbg')
|
||||
except IOError as error:
|
||||
print("Unable to connect to USB device ({})".format(error))
|
||||
|
||||
if not connect_status:
|
||||
print("Unable to connect to USB device")
|
||||
|
||||
housekeeper = housekeepingprotocol.Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol(transport)
|
||||
|
||||
:param library: Transport library to use, currently only 'hidapi' is supported which will use the libusb hidapi
|
||||
:type library: string
|
||||
:returns: Instance of transport layer object
|
||||
:rtype: class:cyhidapi:CyHidApiTransport
|
||||
"""
|
||||
logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
operating_system = platform.system().lower()
|
||||
logger.debug("HID transport using library '{:s}' on OS '{:s}'".format(library, operating_system))
|
||||
|
||||
# HID API is the primary transport
|
||||
if library == 'hidapi':
|
||||
hid_api_supported_os = ['windows', 'darwin', 'linux', 'linux2']
|
||||
if operating_system in hid_api_supported_os:
|
||||
from .cyhidapi import CyHidApiTransport
|
||||
return CyHidApiTransport()
|
||||
|
||||
msg = "System '{0:s}' not implemented for library '{1:s}'".format(operating_system, library)
|
||||
logger.error(msg)
|
||||
raise PyedbglibNotSupportedError(msg)
|
||||
|
||||
# Other transports may include cmsis-dap DLL, atusbhid (dll or so) etc
|
||||
msg = "Transport library '{0}' not implemented.".format(library)
|
||||
logger.error(msg)
|
||||
raise PyedbglibNotSupportedError(msg)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
"""Gathering of all known Microchip CMSIS-DAP debuggers and default EP sizes"""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
# List of known useful HID/CMSIS-DAP tools
|
||||
# 3G tools:
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_JTAGICE3 = 0x2140
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_ATMELICE = 0x2141
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_POWERDEBUGGER = 0x2144
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_EDBG_A = 0x2111
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_ZERO = 0x2157
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_MASS_STORAGE = 0x2169
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_PUBLIC_EDBG_C = 0x216A
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_KRAKEN = 0x2170
|
||||
|
||||
# 4G tools:
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_MEDBG = 0x2145
|
||||
|
||||
# 5G tools:
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_NEDBG_HID_MSD_DGI_CDC = 0x2175
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_PICKIT4_HID_CDC = 0x2177
|
||||
USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_SNAP_HID_CDC = 0x2180
|
||||
|
||||
# The Product String Names are used to identify the tool based on the USB
|
||||
# device product strings (i.e. these names are usually just a subset of the
|
||||
# actual product strings)
|
||||
TOOL_SHORTNAME_TO_USB_PRODUCT_STRING = {
|
||||
'atmelice': "Atmel-ICE",
|
||||
'powerdebugger': "Power Debugger",
|
||||
'pickit4': "MPLAB PICkit 4",
|
||||
'snap': "MPLAB Snap",
|
||||
'nedbg': "nEDBG",
|
||||
'jtagice3': "JTAGICE3",
|
||||
'medbg': "mEDBG",
|
||||
'edbg': "EDBG",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def get_default_report_size(pid):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Retrieve default EP report size based on known PIDs
|
||||
|
||||
:param pid: product ID
|
||||
:return: packet size
|
||||
"""
|
||||
logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
hid_tools = [
|
||||
# 3G
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_JTAGICE3, 'default_report_size': 512},
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_ATMELICE, 'default_report_size': 512},
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_POWERDEBUGGER, 'default_report_size': 512},
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_EDBG_A, 'default_report_size': 512},
|
||||
# 4G
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_MEDBG, 'default_report_size': 64},
|
||||
# 5G
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_NEDBG_HID_MSD_DGI_CDC, 'default_report_size': 64},
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_PICKIT4_HID_CDC, 'default_report_size': 64},
|
||||
{'pid': USB_TOOL_DEVICE_PRODUCT_ID_SNAP_HID_CDC, 'default_report_size': 64}]
|
||||
|
||||
logger.debug("Looking up report size for pid 0x{:04X}".format(pid))
|
||||
for tool in hid_tools:
|
||||
if tool['pid'] == pid:
|
||||
logger.debug("Default report size is {:d}".format(tool['default_report_size']))
|
||||
return tool['default_report_size']
|
||||
logger.debug("PID not found! Reverting to 64b.")
|
||||
return 64
|
||||
|
||||
def tool_shortname_to_product_string_name(shortname):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Mapping for common short names of tools to product string name
|
||||
|
||||
The intention is that this function is always run on the tool name and that the conversion
|
||||
only happens if the name is a known shortname. If the shortname is not known of if the name
|
||||
provided is already a valid Product string name then the provided shortname parameter will
|
||||
just be returned unchanged. So if the name already is a correct Product string name it is
|
||||
still safe to run this conversion funtion on it.
|
||||
|
||||
:param shortname: shortname typically used by atbackend (powerdebugger, atmelice etc.)
|
||||
:return: String to look for in USB product strings to identify the tool
|
||||
"""
|
||||
logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
if shortname is None:
|
||||
logger.debug("Tool shortname is None")
|
||||
# This is also valid as the user might have provided no tool name, but the conversion function
|
||||
# should still be valid
|
||||
return shortname
|
||||
|
||||
shortname_lower = shortname.lower()
|
||||
if shortname_lower not in TOOL_SHORTNAME_TO_USB_PRODUCT_STRING:
|
||||
logger.debug("%s is not a known tool shortname", shortname)
|
||||
# ...but it could be a valid Product string name already so no reason to report an error
|
||||
return shortname
|
||||
|
||||
return TOOL_SHORTNAME_TO_USB_PRODUCT_STRING[shortname_lower]
|
||||
144
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pyedbglib/protocols/avrcmsisdap.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
CMSIS-DAP wrapper for custom commands (using vendor extensions)
|
||||
This mechanism is used to pass JTAGICE3-style commands for AVR devices
|
||||
over the CMSIS-DAP interface
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
from ..util.binary import unpack_be16
|
||||
from ..util import print_helpers
|
||||
from .cmsisdap import CmsisDapUnit
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AvrCommandError(Exception):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Exception type for AVR command-response wrapping
|
||||
"""
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AvrCommand(CmsisDapUnit):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Wraps AVR command and responses
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Vendor Commands used to transport AVR over CMSIS-DAP
|
||||
AVR_COMMAND = 0x80
|
||||
AVR_RESPONSE = 0x81
|
||||
AVR_EVENT = 0x82
|
||||
AVR_MORE_FRAGMENTS = 0x00
|
||||
AVR_FINAL_FRAGMENT = 0x01
|
||||
|
||||
# Retry delay on AVR receive frame
|
||||
AVR_RETRY_DELAY_MS = 50
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport, no_timeouts=False):
|
||||
self.no_timeouts = no_timeouts
|
||||
self.timeout = 1000
|
||||
CmsisDapUnit.__init__(self, transport)
|
||||
self.ep_size = transport.get_report_size()
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Created AVR command on DAP wrapper")
|
||||
|
||||
def poll_events(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Polling for events from AVRs
|
||||
|
||||
:return: response from events
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Polling AVR events")
|
||||
resp = self.dap_command_response(bytearray([self.AVR_EVENT]))
|
||||
return resp
|
||||
|
||||
def _avr_response_receive_frame(self):
|
||||
retries = int(self.timeout / self.AVR_RETRY_DELAY_MS)
|
||||
# Get the delay in seconds
|
||||
delay = self.AVR_RETRY_DELAY_MS / 1000
|
||||
while retries or self.no_timeouts:
|
||||
resp = self.dap_command_response(bytearray([self.AVR_RESPONSE]))
|
||||
if resp[0] != self.AVR_RESPONSE:
|
||||
# Response received is not valid. Abort.
|
||||
raise AvrCommandError("AVR response DAP command failed; invalid token: 0x{:02X}".format(resp[0]))
|
||||
if resp[1] != 0x00:
|
||||
return resp
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Resp: %s", print_helpers.bytelist_to_hex_string(resp))
|
||||
|
||||
# Delay in seconds
|
||||
time.sleep(delay)
|
||||
retries -= 1
|
||||
raise AvrCommandError("AVR response timeout")
|
||||
|
||||
# Chops command up into fragments
|
||||
def _fragment_command_packet(self, command_packet):
|
||||
packets_total = int((len(command_packet) / (self.ep_size - 4)) + 1)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Fragmenting AVR command into {:d} chunks".format(packets_total))
|
||||
fragments = []
|
||||
for i in range(0, packets_total):
|
||||
command_fragment = bytearray([self.AVR_COMMAND, ((i + 1) << 4) + packets_total])
|
||||
if (len(command_packet) - (i * (self.ep_size - 4))) > (self.ep_size - 4):
|
||||
length = self.ep_size - 4
|
||||
else:
|
||||
length = len(command_packet) - (i * (self.ep_size - 4))
|
||||
|
||||
command_fragment.append(int(length >> 8))
|
||||
command_fragment.append(int(length & 0xFF))
|
||||
|
||||
for j in range(0, self.ep_size - 4):
|
||||
if j < length:
|
||||
command_fragment.append(command_packet[i * (self.ep_size - 4) + j])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
command_fragment.append(0x00)
|
||||
|
||||
fragments.append(command_fragment)
|
||||
return fragments
|
||||
|
||||
# Sends an AVR command and waits for response
|
||||
def avr_command_response(self, command):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sends an AVR command and receives a response
|
||||
|
||||
:param command: Command bytes to send
|
||||
:return: Response bytes received
|
||||
"""
|
||||
fragments = self._fragment_command_packet(command)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Sending AVR command")
|
||||
for fragment in fragments:
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Sending AVR command 0x{:02X}".format(fragment[0]))
|
||||
resp = self.dap_command_response(fragment)
|
||||
if resp[0] != self.AVR_COMMAND:
|
||||
raise AvrCommandError("AVR command DAP command failed; invalid token: 0x{:02X}".format(resp[0]))
|
||||
if fragment == fragments[-1]:
|
||||
if resp[1] != self.AVR_FINAL_FRAGMENT:
|
||||
raise AvrCommandError(
|
||||
"AVR command DAP command failed; invalid final fragment ack: 0x{:02X}".format(resp[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if resp[1] != self.AVR_MORE_FRAGMENTS:
|
||||
raise AvrCommandError(
|
||||
"AVR command DAP command failed; invalid non-final fragment ack: 0x{:02X}".format(resp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
# Receive response
|
||||
fragment_info, _, response = self._avr_response_receive_fragment()
|
||||
packets_remaining = (fragment_info & 0xF) - 1
|
||||
for _ in range(0, packets_remaining):
|
||||
fragment_info, _, data = self._avr_response_receive_fragment()
|
||||
response.extend(data)
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
def _avr_response_receive_fragment(self):
|
||||
fragment = []
|
||||
# Receive a frame
|
||||
response = self._avr_response_receive_frame()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the payload size from the header information
|
||||
size = unpack_be16(response[2:4])
|
||||
|
||||
# The message header is 4 bytes, where the last two hold the size of the payload
|
||||
if len(response) < (4 + size):
|
||||
raise AvrCommandError("Response size does not match the header information.")
|
||||
|
||||
# Extract data
|
||||
for i in range(0, size):
|
||||
fragment.append(response[4 + i])
|
||||
|
||||
fragment_info = response[1]
|
||||
return fragment_info, size, fragment
|
||||
543
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pyedbglib/protocols/cmsisdap.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,543 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
CMSIS DAP access protocol
|
||||
|
||||
Interfaces with CMSIS-DAP standard debuggers over HID
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
from .dapwrapper import DapWrapper
|
||||
from ..util import binary
|
||||
from ..pyedbglib_errors import PyedbglibError
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CmsisDapUnit(DapWrapper):
|
||||
"""Communicates with a DAP via standard CMSIS-DAP firmware stack over HID transport"""
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP command constants
|
||||
ID_DAP_Info = 0x00
|
||||
ID_DAP_HostStatus = 0x01
|
||||
ID_DAP_Connect = 0x02
|
||||
ID_DAP_Disconnect = 0x03
|
||||
ID_DAP_TransferConfigure = 0x04
|
||||
ID_DAP_Transfer = 0x05
|
||||
ID_DAP_TransferBlock = 0x06
|
||||
ID_DAP_TransferAbort = 0x07
|
||||
ID_DAP_WriteABORT = 0x08
|
||||
ID_DAP_Delay = 0x09
|
||||
ID_DAP_ResetTarget = 0x0A
|
||||
ID_DAP_SWJ_Pins = 0x10
|
||||
ID_DAP_SWJ_Clock = 0x11
|
||||
ID_DAP_SWJ_Sequence = 0x12
|
||||
ID_DAP_SWD_Configure = 0x13
|
||||
ID_DAP_JTAG_Sequence = 0x14
|
||||
ID_DAP_JTAG_Configure = 0x15
|
||||
ID_DAP_JTAG_IDCODE = 0x16
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP responses
|
||||
DAP_OK = 0x00
|
||||
DAP_ERROR = 0xff
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP info fields
|
||||
DAP_ID_VENDOR = 0x01
|
||||
DAP_ID_PRODUCT = 0x02
|
||||
DAP_ID_SER_NUM = 0x03
|
||||
DAP_ID_FW_VER = 0x04
|
||||
DAP_ID_DEVICE_VENDOR = 0x05
|
||||
DAP_ID_DEVICE_NAME = 0x06
|
||||
DAP_ID_CAPABILITIES = 0xF0
|
||||
DAP_ID_PACKET_COUNT = 0xFE
|
||||
DAP_ID_PACKET_SIZE = 0xFF
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP ports
|
||||
DAP_PORT_AUTODETECT = 0
|
||||
DAP_PORT_DISABLED = 0
|
||||
DAP_PORT_SWD = 1
|
||||
DAP_PORT_JTAG = 2
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
DapWrapper.__init__(self, transport)
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_response(self, cmd, rsp):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks that the response echoes the command
|
||||
|
||||
:param cmd: command going in
|
||||
:param rsp: response coming out
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Checking response: cmd=0x%02X rsp=0x%02X", cmd[0], rsp[0])
|
||||
if cmd[0] != rsp[0]:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Invalid response header")
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_info(self):
|
||||
"""Collects the dap info"""
|
||||
info = {
|
||||
'vendor': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_VENDOR),
|
||||
'product': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_PRODUCT),
|
||||
'serial': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_SER_NUM),
|
||||
'fw': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_FW_VER),
|
||||
'device_vendor': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_DEVICE_VENDOR),
|
||||
'device_name': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_DEVICE_NAME),
|
||||
'capabilities': self._dap_info_field(self.DAP_ID_CAPABILITIES)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return info
|
||||
|
||||
def _dap_info_field(self, field):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Queries one field from the dap info
|
||||
|
||||
:param field: which field to query
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_info (%d)", field)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_Info
|
||||
cmd[1] = field
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
return (rsp[2:rsp[1] + 2].decode()).strip('\0')
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_led(self, index, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Operates the LED
|
||||
|
||||
:param index: which led
|
||||
:param state: what to do with it
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_led (%d, %d)", index, state)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(3)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_HostStatus
|
||||
cmd[1] = index
|
||||
cmd[2] = state
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_connect(self):
|
||||
"""Connects to the DAP"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_connect (SWD)")
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_Connect
|
||||
cmd[1] = self.DAP_PORT_SWD
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_PORT_SWD:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Connect failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_disconnect(self):
|
||||
"""Disconnects from the DAP"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_disconnect")
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(1)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_Disconnect
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CmsisDapDebugger(CmsisDapUnit):
|
||||
"""ARM-specific cmsis-dap implementation"""
|
||||
|
||||
# SWJ pin IDs
|
||||
DAP_SWJ_SWCLK_TCK = (1 << 0)
|
||||
DAP_SWJ_SWDIO_TMS = (1 << 1)
|
||||
DAP_SWJ_TDI = (1 << 2)
|
||||
DAP_SWJ_TDO = (1 << 3)
|
||||
DAP_SWJ_nTRST = (1 << 5)
|
||||
DAP_SWJ_nRESET = (1 << 7)
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP transfer types
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP = (1 << 0)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_RnW = (1 << 1)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_A2 = (1 << 2)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_A3 = (1 << 3)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_MATCH_VALUE = (1 << 4)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_MATCH_MASK = (1 << 5)
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP transfer responses
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_INVALID = 0
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_OK = (1 << 0)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_WAIT = (1 << 1)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_FAULT = (1 << 2)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_ERROR = (1 << 3)
|
||||
DAP_TRANSFER_MISMATCH = (1 << 4)
|
||||
|
||||
# DP definitions
|
||||
DP_IDCODE = 0x00
|
||||
DP_ABORT = 0x00
|
||||
DP_CTRL_STAT = 0x04
|
||||
DP_WCR = 0x04
|
||||
DP_SELECT = 0x08
|
||||
DP_RESEND = 0x08
|
||||
DP_RDBUFF = 0x0C
|
||||
|
||||
# JTAG-specific codes
|
||||
JTAG_ABORT = 0x08
|
||||
JTAG_DPACC = 0x0A
|
||||
JTAG_APACC = 0x0B
|
||||
JTAG_IDCODE = 0x0E
|
||||
JTAG_BYPASS = 0x0F
|
||||
|
||||
# SWD-specific codes
|
||||
SWD_AP_CSW = 0x00
|
||||
SWD_AP_TAR = 0x04
|
||||
SWD_AP_DRW = 0x0C
|
||||
|
||||
# TAR size
|
||||
TAR_MAX = 0x400
|
||||
|
||||
# DAP CTRL_STAT bits
|
||||
# Source: Coresight Techref
|
||||
CSYSPWRUPACK = (1 << 31)
|
||||
CSYSPWRUPREQ = (1 << 30)
|
||||
CDBGPWRUPACK = (1 << 29)
|
||||
CDBGPWRUPREQ = (1 << 28)
|
||||
CDBGRSTACK = (1 << 27)
|
||||
CDBGRSTREQ = (1 << 26)
|
||||
WDATAERR = (1 << 7)
|
||||
READOK = (1 << 6)
|
||||
STICKYERR = (1 << 5)
|
||||
STICKYCMP = (1 << 4)
|
||||
TRNMODE = (1 << 2)
|
||||
STICKYORUN = (1 << 1)
|
||||
ORUNDETECT = (1 << 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Useful CSW settings
|
||||
CSW_32BIT = 0x02
|
||||
CSW_16BIT = 0x01
|
||||
CSW_8BIT = 0x00
|
||||
CSW_ADDRINC_OFF = 0x00
|
||||
CSW_ADDRINC_ON = (1 << 4)
|
||||
|
||||
# Supported DAP IDs.
|
||||
CM0P_DAPID = 0x0BC11477
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
CmsisDapUnit.__init__(self, transport)
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_swj_clock(self, clock):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sets up the SWD clock timing
|
||||
|
||||
:param clock: clock value in Hz
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_swj_clk (%d)", clock)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(1)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_SWJ_Clock
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le32(clock))
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("SWJ clock setting failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_transfer_configure(self, idle, count, retry):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Configures SWD transfers
|
||||
|
||||
:param idle: idle cycles
|
||||
:param count: retry count
|
||||
:param retry: match retry value
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_transfer_configure (%d, %d, %d)", idle, count, retry)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_TransferConfigure
|
||||
cmd[1] = idle
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le16(count))
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le16(retry))
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Transfer configure failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_swd_configure(self, cfg):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Configures the SWD interface
|
||||
|
||||
:param cfg: turnaround and data phase config parameters
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_swd_configure (%d)", cfg)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_SWD_Configure
|
||||
cmd[1] = cfg
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("SWD configure failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_reset_target(self):
|
||||
"""Reset the target using the DAP"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_reset_target")
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(1)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_ResetTarget
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Reset target failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_read_reg(self, reg):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reads a DAP AP/DP register
|
||||
|
||||
:param reg: register to read
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_read_reg (0x%02X)", reg)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(8)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_Transfer
|
||||
cmd[1] = 0x00 # dap
|
||||
cmd[2] = 0x01 # 1 word
|
||||
cmd[3] = reg | self.DAP_TRANSFER_RnW
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != 1 or rsp[2] != self.DAP_TRANSFER_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Read reg failed (0x{0:02X}, {1:02X})".format(rsp[1], rsp[2]))
|
||||
value = binary.unpack_le32(rsp[3:7])
|
||||
return value
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_write_reg(self, reg, value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Writes a DAP AP/DP register
|
||||
|
||||
:param reg: register to write
|
||||
:param value: value to write
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_write_reg (0x%02X) = 0x%08X", reg, value)
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(4)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_Transfer
|
||||
cmd[1] = 0x00 # dap
|
||||
cmd[2] = 0x01 # 1 word
|
||||
cmd[3] = reg
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le32(value))
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != 1 or rsp[2] != self.DAP_TRANSFER_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Write reg failed (0x{0:02X}, {1:02X})".format(rsp[1], rsp[2]))
|
||||
|
||||
def read_word(self, address):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reads a word from the device memory bus
|
||||
|
||||
:param address: address to read
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("read word at 0x%08X", address)
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.SWD_AP_TAR | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP, address)
|
||||
return self.dap_read_reg(self.SWD_AP_DRW | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP)
|
||||
|
||||
def write_word(self, address, data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Writes a word to the device memory bus
|
||||
|
||||
:param address: address to write
|
||||
:param data: data to write
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("write word at 0x%08X = 0x%08X", address, data)
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.SWD_AP_TAR | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP, address)
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.SWD_AP_DRW | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP, data)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def multiple_of_four(x):
|
||||
""" 4 byte boundary """
|
||||
return x & ~0x03
|
||||
|
||||
def read_block(self, address, numbytes):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reads a block from the device memory bus
|
||||
|
||||
:param address: byte address
|
||||
:param numbytes: number of bytes
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Block read of %d bytes at address 0x%08X", numbytes, address)
|
||||
# Collect results here
|
||||
result = bytearray()
|
||||
# In chunks of (len-header)
|
||||
max_payload_size_bytes = self.multiple_of_four(self.transport.get_report_size() - 5)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Max payload size of %d bytes", max_payload_size_bytes)
|
||||
while numbytes:
|
||||
# Calculate read size
|
||||
read_size_bytes = max_payload_size_bytes
|
||||
|
||||
# Last chunk?
|
||||
if read_size_bytes > numbytes:
|
||||
read_size_bytes = numbytes
|
||||
|
||||
# Too large for TAR?
|
||||
tar_max_chunk = self.TAR_MAX - (address - (address & (1-self.TAR_MAX)))
|
||||
if read_size_bytes > tar_max_chunk:
|
||||
read_size_bytes = tar_max_chunk
|
||||
|
||||
# Log
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Read %d bytes from TAR address 0x%08X", read_size_bytes, address)
|
||||
|
||||
# Set TAR
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.SWD_AP_TAR | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP, address)
|
||||
|
||||
# Read chunk
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_TransferBlock
|
||||
cmd[1] = 0x00
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le16(read_size_bytes // 4))
|
||||
cmd.extend([self.SWD_AP_DRW | self.DAP_TRANSFER_RnW | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP])
|
||||
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check outcome
|
||||
if rsp[3] != self.DAP_TRANSFER_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Transfer failed (0x{0:02X}) address 0x{1:08X}".format(rsp[3], address))
|
||||
|
||||
# Extract payload
|
||||
num_words_read = binary.unpack_le16(rsp[1:3])
|
||||
|
||||
# Check
|
||||
if num_words_read * 4 != read_size_bytes:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError(
|
||||
"Unexpected number of bytes returned from block read ({0:d} != {1:d})".format(num_words_read * 4,
|
||||
read_size_bytes))
|
||||
|
||||
# Extend results
|
||||
result.extend(rsp[4:4 + read_size_bytes])
|
||||
numbytes -= read_size_bytes
|
||||
address += read_size_bytes
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
def write_block(self, address, data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Writes a block to the device memory bus
|
||||
|
||||
:param address: byte address
|
||||
:param data: data
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Block write of %d bytes at address 0x%08X", len(data), address)
|
||||
|
||||
# In chunks of (len-header)
|
||||
max_payload_size_bytes = self.multiple_of_four(self.transport.get_report_size() - 5)
|
||||
while data:
|
||||
# Calculate write size
|
||||
write_size_bytes = max_payload_size_bytes
|
||||
if write_size_bytes > len(data):
|
||||
write_size_bytes = len(data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Too large for TAR?
|
||||
tar_max_chunk = self.TAR_MAX - (address - (address & (1 - self.TAR_MAX)))
|
||||
if write_size_bytes > tar_max_chunk:
|
||||
write_size_bytes = tar_max_chunk
|
||||
|
||||
# Set TAR
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.SWD_AP_TAR | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP, address)
|
||||
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_TransferBlock
|
||||
cmd[1] = 0x00
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le16(write_size_bytes // 4))
|
||||
cmd.extend([self.SWD_AP_DRW | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP])
|
||||
cmd.extend(data[0:write_size_bytes])
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
|
||||
# Shrink data buffer
|
||||
data = data[write_size_bytes:]
|
||||
address += write_size_bytes
|
||||
|
||||
def _send_flush_tms(self):
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_SWJ_Sequence
|
||||
cmd[1] = 7 * 8
|
||||
for _ in range(7):
|
||||
cmd.extend([0xff])
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("SWJ sequence failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
def init_swj(self):
|
||||
"""Magic sequence to execute on pins to enable SWD in case of JTAG-default parts"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("SWJ init sequence")
|
||||
# According to ARM manuals:
|
||||
# Send at least 50 cycles with TMS=1
|
||||
self._send_flush_tms()
|
||||
|
||||
# Send 16-bit switching code
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(2)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_SWJ_Sequence
|
||||
cmd[1] = 16
|
||||
cmd.extend(binary.pack_le16(0xE79E))
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("SWJ sequence failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
# Flush TMS again
|
||||
self._send_flush_tms()
|
||||
|
||||
# Set data low again
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(3)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_SWJ_Sequence
|
||||
cmd[1] = 1
|
||||
cmd[2] = 0x00
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
if rsp[1] != self.DAP_OK:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("SWJ sequence failed (0x{0:02X})".format(rsp[1]))
|
||||
|
||||
# Now read the ID to check that it has switched
|
||||
dap_id = self.dap_read_idcode()
|
||||
if dap_id != self.CM0P_DAPID:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Invalid SWD DAP ID code! Only M0+ is currently supported.")
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_read_idcode(self):
|
||||
"""Reads the IDCODE from the SWD DP"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("reading swd idcode")
|
||||
return self.dap_read_reg(self.DP_IDCODE)
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_target_init(self):
|
||||
"""Configures the DAP for use"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_target_init")
|
||||
# Clear all stickies
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.DP_ABORT, self.STICKYERR | self.STICKYCMP | self.STICKYORUN)
|
||||
# Select to 0
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.DP_SELECT, 0)
|
||||
# Request debug power
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.DP_CTRL_STAT, self.CDBGPWRUPREQ | self.CSYSPWRUPREQ)
|
||||
# Most useful default of 32-bit word access with auto-increment enabled
|
||||
self.dap_write_reg(self.SWD_AP_CSW | self.DAP_TRANSFER_APnDP, self.CSW_ADDRINC_ON | self.CSW_32BIT)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CmsisDapSamDebugger(CmsisDapDebugger):
|
||||
"""SAM specific CMSIS-DAP debugger"""
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_reset_ext(self, extend=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reset the target using the hardware
|
||||
|
||||
Some SAM devices (for example SAMDx and SAMLx) have an additional 'reset extension' capability which is not part
|
||||
of the CMSIS-DAP standard. It is used to prevent the device from running after reset and then overriding its
|
||||
SWD IO. The procedure is simply to hold SW_CLK low while releasing /RESET. This is done here using SWJ pins
|
||||
function IF the extend argument is set.
|
||||
|
||||
:param extend: boolean flag to extend reset
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("dap_reset_ext")
|
||||
cmd = bytearray(7)
|
||||
cmd[0] = self.ID_DAP_SWJ_Pins
|
||||
cmd[1] = 0 # Reset LOW, TCK LOW
|
||||
cmd[2] = self.DAP_SWJ_nRESET
|
||||
if extend:
|
||||
cmd[2] |= self.DAP_SWJ_SWCLK_TCK
|
||||
cmd[3] = 0
|
||||
cmd[4] = 0
|
||||
cmd[5] = 0
|
||||
cmd[6] = 0
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
|
||||
cmd[1] = self.DAP_SWJ_nRESET # Reset high, TCK still low
|
||||
cmd[2] = self.DAP_SWJ_nRESET
|
||||
if extend:
|
||||
cmd[2] |= self.DAP_SWJ_SWCLK_TCK
|
||||
|
||||
rsp = self.dap_command_response(cmd)
|
||||
self._check_response(cmd, rsp)
|
||||
|
||||
# Allow Reset to be pulled high
|
||||
time.sleep(0.1)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
"""Wrapper for any protocol over CMSIS-DAP"""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DapWrapper(object):
|
||||
"""Base class for any CMSIS-DAP protocol wrapper"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.transport = transport
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Created DapWrapper")
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_command_response(self, packet):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Send a command, receive a response
|
||||
|
||||
:param packet: bytes to send
|
||||
:return: response received
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.transport.hid_transfer(packet)
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_command_write(self, packet):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Send a packet
|
||||
|
||||
:param packet: packed data to sent
|
||||
:return: bytes sent
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.transport.hid_write(packet)
|
||||
|
||||
def dap_command_read(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Receive data
|
||||
|
||||
:return: data received
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.transport.hid_read()
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
|
||||
"""Implements EDBG Protocol, a sub-protocol in the JTAGICE3 family of protocols."""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
from ..util.binary import unpack_be16
|
||||
from .jtagice3protocol import Jtagice3Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EdbgProtocol(Jtagice3Protocol):
|
||||
"""Implements EDBG protocol functionality on the JTAGICE3 protocol family"""
|
||||
|
||||
CMD_EDBG_QUERY = 0x00 # Capability discovery
|
||||
CMD_EDBG_SET = 0x01 # Set parameters
|
||||
CMD_EDBG_GET = 0x02 # Get parameters
|
||||
|
||||
CMD_EDBG_PROGRAM_ID_CHIP = 0x50 # Programs an ID chip
|
||||
CMD_EDBG_REFRESH_ID_CHIP = 0x51 # Triggers ID chip refresh
|
||||
CMD_EDBG_READ_ID_CHIP = 0x7E # Retrieve ID chip info
|
||||
|
||||
AVR_GET_CONFIG = 0x83 # CMSIS vendor 3 get config command
|
||||
|
||||
RSP_EDBG_OK = 0x80 # All OK
|
||||
RSP_EDBG_LIST = 0x81 # List of items returned
|
||||
RSP_EDBG_DATA = 0x84 # Data returned
|
||||
RSP_EDBG_FAILED = 0xA0 # Command failed to execute
|
||||
|
||||
EDBG_QUERY_COMMANDS = 0x00
|
||||
|
||||
EDBG_CTXT_CONTROL = 0x00 # Control
|
||||
EDBG_CONTROL_LED_USAGE = 0x00
|
||||
EDBG_CONTROL_EXT_PROG = 0x01
|
||||
EDBG_CONTROL_TARGET_POWER = 0x10
|
||||
|
||||
EDBG_CONFIG_KIT_DATA = 0x20 # Read the kit info flash page
|
||||
|
||||
"""Mapping EDBG error codes to more human friendly strings"""
|
||||
EDBG_ERRORS = {0: 'SUCCESS'}
|
||||
|
||||
"""Mapping SHA204 response codes to more human friendly strings"""
|
||||
RESPONSE_CODE = {0x00: 'SHA204_SUCCESS',
|
||||
0xD2: 'SHA204_PARSE_ERROR',
|
||||
0xD3: 'SHA204_CMD_FAIL',
|
||||
0xD4: 'SHA204_STATUS_CRC',
|
||||
0xE0: 'SHA204_FUNC_FAIL',
|
||||
0xE2: 'SHA204_BAD_PARAM',
|
||||
0xE4: 'SHA204_INVALID_SIZE',
|
||||
0xE5: 'SHA204_BAD_CRC',
|
||||
0xE6: 'SHA204_RX_FAIL',
|
||||
0xE7: 'SHA204_RX_NO_RESPONSE',
|
||||
0xE8: 'SHA204_RESYNC_WITH_WAKEUP',
|
||||
0xF0: 'SHA204_COMM_FAIL',
|
||||
0xF1: 'SHA204_TIMEOUT',
|
||||
0xFA: 'ID_DATA_LOCKED',
|
||||
0xFB: 'ID_CONFIG_LOCKED',
|
||||
0xFC: 'ID_INVALID_SLOT',
|
||||
0xFD: 'ID_DATA_PARSING_ERROR',
|
||||
0xFE: 'ID_DATA_NOT_EQUAL'}
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport):
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
super(EdbgProtocol, self).__init__(
|
||||
transport, Jtagice3Protocol.HANDLER_EDBG)
|
||||
|
||||
def check_command_exists(self, command):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if command is supported
|
||||
|
||||
Runs a query to the tool to get a list of supported commands, then looks for
|
||||
the input command in the list. If not supported, it raises NotImplementedError.
|
||||
|
||||
:param command: The command to test.
|
||||
:return: None
|
||||
"""
|
||||
commands_supported = self.query(self.EDBG_QUERY_COMMANDS)
|
||||
if command not in commands_supported:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("Invalid command: 0x{:02X}".format(command))
|
||||
|
||||
def error_as_string(self, code):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the response error as a string (error code translated to descriptive string)
|
||||
|
||||
:param code: error code
|
||||
:return: error code as descriptive string
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return self.EDBG_ERRORS[code]
|
||||
except KeyError:
|
||||
return "Unknown error!"
|
||||
|
||||
def response_as_string(self, code):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the response code as a string (response code translated to descriptive string)
|
||||
|
||||
:param code: response code
|
||||
:return: error code as descriptive string
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return self.RESPONSE_CODE[code]
|
||||
except KeyError:
|
||||
return "Unknown response!"
|
||||
|
||||
def program_id_chip(self, id_number, data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Program the connected ID device located at the id_number with data.
|
||||
|
||||
:param id_number: Extension header ID number (Range 1 - 16)
|
||||
:param data: A 64-byte data array to be programmed
|
||||
:return: Response status from the programming
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.info("Programming ID chip...")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.check_command_exists(self.CMD_EDBG_PROGRAM_ID_CHIP)
|
||||
except NotImplementedError as err:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Non-compliant command: %s", err)
|
||||
|
||||
# Old EDBG implementations contained a non-compliant version of this command
|
||||
# Version 0 command
|
||||
packet = bytearray([self.CMD_EDBG_PROGRAM_ID_CHIP, self.CMD_VERSION0, id_number - 1] + data)
|
||||
resp = self.jtagice3_command_response_raw(packet)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Program ID response: %s", self.response_as_string(resp[3]))
|
||||
return resp[3]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Version 1 command
|
||||
packet = bytearray([self.CMD_EDBG_PROGRAM_ID_CHIP, self.CMD_VERSION1, id_number] + data)
|
||||
status = self.check_response(self.jtagice3_command_response(packet))
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Program ID response: %s", self.response_as_string(status[0]))
|
||||
return status[0]
|
||||
|
||||
def refresh_id_chip(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Forces a refresh of the list of connected ID devices.
|
||||
|
||||
:return: None
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.info("Refreshing ID chip...")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.check_command_exists(self.CMD_EDBG_REFRESH_ID_CHIP)
|
||||
except NotImplementedError as err:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Non-compliant command: %s", err)
|
||||
|
||||
# Old EDBG implementations contained a non-compliant version of this command
|
||||
# Version 0 command
|
||||
packet = bytearray([self.CMD_EDBG_REFRESH_ID_CHIP, self.CMD_VERSION0])
|
||||
resp = self.jtagice3_command_response_raw(packet)
|
||||
if not resp[3] == self.RSP_EDBG_OK:
|
||||
raise IOError("Invalid response from CMD_EDBG_REFRESH_ID_CHIP")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Version 1 command
|
||||
packet = bytearray([self.CMD_EDBG_REFRESH_ID_CHIP, self.CMD_VERSION1])
|
||||
self.check_response(self.jtagice3_command_response(packet))
|
||||
|
||||
def read_id_chip(self, id_number):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reads the ID information from the ID chip connected at id_number
|
||||
|
||||
:param id_number: Extension header ID number (Range 1 - 16)
|
||||
:return: A 64-byte data array
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.info("Reading ID chip...")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.check_command_exists(self.CMD_EDBG_READ_ID_CHIP)
|
||||
except NotImplementedError as err:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Non-compliant command: %s", err)
|
||||
|
||||
# Old EDBG implementations contained a non-compliant version of this command
|
||||
# Version 0 command
|
||||
packet = bytearray([self.CMD_EDBG_READ_ID_CHIP, self.CMD_VERSION0, id_number - 1])
|
||||
resp = self.jtagice3_command_response_raw(packet)
|
||||
if resp[4] == self.RSP_EDBG_DATA:
|
||||
return resp[6:]
|
||||
return False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Version 1 command
|
||||
packet = bytearray([self.CMD_EDBG_READ_ID_CHIP, self.CMD_VERSION1, id_number])
|
||||
data = self.check_response(self.jtagice3_command_response(packet))
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
def read_edbg_extra_info(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Reads the kit info flash page, containing board specific data
|
||||
|
||||
:return: A data array containing the kit info
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.info("Reading kit info...")
|
||||
|
||||
# The second parameter tells the debugger it is the only command
|
||||
# The last parameter tells what to read. If zero a whole page is read, and
|
||||
# if non-zero 32-bytes is fetched from offset 32 * parameter. The parameter
|
||||
# cannot be greater than 8
|
||||
response = self.dap_command_response(bytearray([self.AVR_GET_CONFIG, 0x01,
|
||||
self.EDBG_CONFIG_KIT_DATA, 0x0]))
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove unused data
|
||||
if len(response) >= 256 + 6:
|
||||
self.logger.info("Response size is truncated")
|
||||
response = response[:256 + 6]
|
||||
|
||||
# Byte 0 will echo the current command
|
||||
# Byte 1 show the command status
|
||||
if response[0] == self.AVR_GET_CONFIG:
|
||||
|
||||
# Check the status code
|
||||
if response[1] == 0:
|
||||
# Bytes [3..2] contain the received size
|
||||
size = unpack_be16(response[2:4])
|
||||
return response[6:size]
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Command failed with error: %i", response[1])
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Command was not echoed back")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
"""Implements Housekeeping Protocol, a sub-protocol in the JTAGICE3 family of protocols."""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
from .jtagice3protocol import Jtagice3Protocol
|
||||
from .jtagice3protocol import Jtagice3ResponseError
|
||||
from ..util import binary
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol(Jtagice3Protocol):
|
||||
"""Implements housekeeping functionality on the JTAGICE3 protocol family"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Query contexts
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_QUERY_COMMANDS = 0x00 # List supported commands
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_QUERY_ANALOG_CHANNELS = 0x01 # List which analog channels are present
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_QUERY_SPECIAL_ABILITIES = 0x02 # List special abilities
|
||||
|
||||
# Protocol commands
|
||||
CMD_HOUSEKEEPING_START_SESSION = 0x10 # Sign on
|
||||
CMD_HOUSEKEEPING_END_SESSION = 0x11 # Sign off
|
||||
CMD_HOUSEKEEPING_FW_UPGRADE = 0x50 # Enter upgrade mode
|
||||
|
||||
# Get/Set contexts
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG = 0x00 # Configuration parameters
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_ANALOG = 0x01 # Analog parameters
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_STATEMENT = 0x02 # Statement memory (deprecated)
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_USB = 0x03 # USB parameters
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_STATISTICS = 0x80 # Statistics
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_DIAGNOSTICS = 0x81 # Diagnostics
|
||||
|
||||
# Config context
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_HWREV = 0x00 # Hardware version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_FWREV_MAJ = 0x01 # Major firmware version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_FWREV_MIN = 0x02 # Minor firmware version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_BUILD = 0x03 # Build number (2 bytes)
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_CHIP = 0x05 # Chipset ID
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_BLDR_MAJ = 0x06 # Bootloader major version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_BLDR_MIN = 0x07 # Bootloader minor version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_DEBUG_BUILD = 0x08 # Debug build flag
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_FIRMWARE_IMAGE = 0x09 # Firmware Image enumerator
|
||||
|
||||
# USB context
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_USB_MAX_READ = 0x00 # Maximum USB read block size
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_USB_MAX_WRITE = 0x01 # Maximum USB write block size
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_USB_EP_SIZE_HID = 0x10 # Current HID endpoint size
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_USB_EP_SIZE_CDC = 0x11 # Current CDC endpoint size
|
||||
|
||||
# Diagnostics
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_DIAGNOSTICS_RESET_CAUSE = 0x00 # Last reset cause
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_DIAGNOSTICS_BOD_CTRL = 0x01 # BOD register
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_HOST_ID = 0x02 # Debugger host device identifier
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_HOST_REV = 0x03 # Debugger host device revision
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_MODULE_VER_JTAG = 0x04 # Debugger host JTAG master version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_MODULE_VER_AW = 0x05 # Debugger host aWire master version
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_DIAGNOSTICS_CPU_CLK = 0x06 # Debugger host CPU clock speed
|
||||
|
||||
# Analog
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_ANALOG_VTREF = 0x00 # Target voltage reference value
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_ANALOG_VTG_BUF = 0x01 # Bufferred target voltage reference
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_ANALOG_VUSB = 0x02 # USB voltage
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_TSUP_VOLTAGE = 0x20 # Target supply voltage setpoint
|
||||
|
||||
# Special Abilities
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_ABILITY_RESET_EXTENSION = 0x00 # This tool is capable of reset extension
|
||||
HOUSEKEEPING_ABILITY_HV_UPDI_ENABLE = 0x10 # This tool is capable of UPDI high-voltage activation
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport):
|
||||
super(Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol, self).__init__(transport, Jtagice3Protocol.HANDLER_HOUSEKEEPING)
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Created AVR housekeeping protocol")
|
||||
|
||||
def list_supported_commands(self):
|
||||
"""Uses the query interface to list all supported commands"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Querying commands supported by this instance of housekeeping handler")
|
||||
commands = self.query(self.HOUSEKEEPING_QUERY_COMMANDS)
|
||||
return commands
|
||||
|
||||
# Direct protocol commands
|
||||
def start_session(self):
|
||||
"""Starts a session with the debugger (sign-on)"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Housekeeping::start_session")
|
||||
response = self.jtagice3_command_response(bytearray([self.CMD_HOUSEKEEPING_START_SESSION, self.CMD_VERSION0]))
|
||||
self.check_response(response)
|
||||
|
||||
def end_session(self, reset_tool=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Ends a session with the debugger (sign-off)
|
||||
|
||||
:param reset_tool: resets the hardware
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Housekeeping::end_session")
|
||||
response = self.jtagice3_command_response(
|
||||
bytearray([self.CMD_HOUSEKEEPING_END_SESSION, self.CMD_VERSION0, 1 if reset_tool else 0]))
|
||||
self.check_response(response)
|
||||
|
||||
def enter_upgrade_mode(self, key=0x31727C10):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Puts the debugger into firmware upgrade mode
|
||||
|
||||
:param key: upgrade key
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Housekeeping::enter_upgrade_mode")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = self.jtagice3_command_response(
|
||||
bytearray([self.CMD_HOUSEKEEPING_FW_UPGRADE, self.CMD_VERSION0]) + binary.pack_be32(key))
|
||||
except IOError:
|
||||
self.logger.debug("IOError on enter upgrade mode. Device rebooted before response was read.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.check_response(response)
|
||||
|
||||
def read_version_info(self):
|
||||
"""Reads version info from the debugger"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Housekeeping::reading version info")
|
||||
|
||||
# Results in dict form
|
||||
versions = {
|
||||
# HW version
|
||||
'hardware': self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_HWREV),
|
||||
# FW version
|
||||
'firmware_major': self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_FWREV_MAJ),
|
||||
'firmware_minor': self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_FWREV_MIN),
|
||||
'build': self.get_le16(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_BUILD),
|
||||
# BLDR
|
||||
'bootloader': self.get_le16(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_BLDR_MAJ),
|
||||
# Host info
|
||||
'chip': self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_CHIP),
|
||||
'host_id': self.get_le32(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_DIAGNOSTICS, self.HOUSEKEEPING_HOST_ID),
|
||||
'host_rev': self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_DIAGNOSTICS, self.HOUSEKEEPING_HOST_REV),
|
||||
# Misc
|
||||
'debug': self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_DEBUG_BUILD)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Firmware Image Requirement Enumerator is only supported on some tools
|
||||
try:
|
||||
versions['fire'] = self.get_byte(self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONTEXT_CONFIG, self.HOUSEKEEPING_CONFIG_FIRMWARE_IMAGE)
|
||||
except Jtagice3ResponseError:
|
||||
versions['fire'] = None
|
||||
|
||||
return versions
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,337 @@
|
||||
"""JTAGICE3 protocol mappings"""
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
from .avrcmsisdap import AvrCommand
|
||||
from ..util import binary
|
||||
from ..util import print_helpers
|
||||
from ..pyedbglib_errors import PyedbglibError
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Jtagice3Command(AvrCommand):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sends a "JTAGICE3" command frame, and received a response
|
||||
|
||||
JTAGICE3 protocol header is formatted:
|
||||
JTAGICE3_TOKEN 0x0E
|
||||
PROTOCOL_VERSION 0
|
||||
SEQUENCE_NUMBER_L
|
||||
SEQUENCE_NUMBER_H
|
||||
HANDLER_ID
|
||||
PAYLOAD
|
||||
|
||||
Response format is:
|
||||
JTAGICE3_TOKEN 0x0E
|
||||
SEQUENCE_NUMBER_L echo
|
||||
SEQUENCE_NUMBER_H echo
|
||||
HANDLER_ID
|
||||
PAYLOAD
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# JTAGICE3 protocol token
|
||||
JTAGICE3_TOKEN = 0x0E
|
||||
JTAGICE3_PROTOCOL_VERSION = 0x00
|
||||
|
||||
# Handlers within JTAGICE3 protocol
|
||||
HANDLER_DISCOVERY = 0x00
|
||||
HANDLER_HOUSEKEEPING = 0x01
|
||||
HANDLER_SPI = 0x11
|
||||
HANDLER_AVR8_GENERIC = 0x12
|
||||
HANDLER_AVR32_GENERIC = 0x13
|
||||
HANDLER_TPI = 0x14
|
||||
HANDLER_EDBG = 0x20
|
||||
HANDLER_COPROCESSOR = 0x21
|
||||
HANDLER_POWER = 0x22
|
||||
HANDLER_SELFTEST = 0x81
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport, handler):
|
||||
super(Jtagice3Command, self).__init__(transport)
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Created JTAGICE3 command")
|
||||
self.handler = handler
|
||||
self.sequence_id = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def validate_response(self, response):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Validates the response form the debugger
|
||||
|
||||
:param response: raw response bytes
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Checking response (%s)", print_helpers.bytelist_to_hex_string(response))
|
||||
|
||||
# Check length first
|
||||
if len(response) < 5:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Invalid response length ({:d}).".format(len(response)))
|
||||
|
||||
# Check token
|
||||
if response[0] != self.JTAGICE3_TOKEN:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Invalid token (0x{:02X}) in response.".format(response[0]))
|
||||
|
||||
# Check sequence
|
||||
sequence = response[1] + (response[2] << 8)
|
||||
if self.sequence_id != sequence:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError(
|
||||
"Invalid sequence in response (0x{:04X} vs 0x{:04X}).".format(self.sequence_id, sequence))
|
||||
|
||||
# Check handler
|
||||
if response[3] != self.handler:
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError("Invalid handler (0x{:02X}) in response.".format(response[3]))
|
||||
|
||||
def jtagice3_command_response_raw(self, command):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sends a JTAGICE3 command and receives the corresponding response
|
||||
|
||||
:param command:
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Header
|
||||
header = bytearray([self.JTAGICE3_TOKEN, self.JTAGICE3_PROTOCOL_VERSION, self.sequence_id & 0xFF,
|
||||
(self.sequence_id >> 8) & 0xFF, self.handler])
|
||||
|
||||
# Send command, receive response
|
||||
packet = header + bytearray(command)
|
||||
response = self.avr_command_response(packet)
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
def jtagice3_command_response(self, command):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sends a JTAGICE3 command and receives the corresponding response, and validates it
|
||||
|
||||
:param command:
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
response = self.jtagice3_command_response_raw(command)
|
||||
|
||||
# Increment sequence number
|
||||
self.sequence_id += 1
|
||||
if self.sequence_id > 0xFFFE:
|
||||
self.sequence_id = 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Peel and return
|
||||
return response[4:]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Jtagice3ResponseError(Exception):
|
||||
"""Exception type for JTAGICE3 responses"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, msg, code):
|
||||
super(Jtagice3ResponseError, self).__init__(msg)
|
||||
# self.message = msg
|
||||
self.code = code
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Jtagice3Protocol(Jtagice3Command):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Base class for all protocols in the JTAGICE3 family.
|
||||
|
||||
All sub-protocols support query, get and set commands.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Command versioning
|
||||
CMD_VERSION0 = 0
|
||||
CMD_VERSION1 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
# All handler share these functions:
|
||||
CMD_QUERY = 0x00
|
||||
CMD_SET = 0x01
|
||||
CMD_GET = 0x02
|
||||
|
||||
# And these base responses
|
||||
PROTOCOL_OK = 0x80
|
||||
PROTOCOL_LIST = 0x81
|
||||
PROTOCOL_DATA = 0x84
|
||||
PROTOCOL_FAILED = 0xA0
|
||||
# PROTOCOL_FAILED_WITH_DATA = 0xA1
|
||||
|
||||
# Failure codes
|
||||
FAILURE_OK = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# CMD_SET and CMD_GET failure codes
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_OK = 0x00
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 0x10
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_NOT_SUPPORTED = 0x11
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_INVALID_CLOCK_SPEED = 0x20
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_ILLEGAL_STATE = 0x21
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_JTAGM_INIT_ERROR = 0x22
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_INVALID_VALUE = 0x23
|
||||
SETGET_FAILURE_HANDLER_ERROR = 0x30
|
||||
|
||||
"""Mapping JTAGICE3 error codes to more human friendly strings"""
|
||||
JTAGICE3_ERRORS = {0: 'SUCCESS'}
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, transport, handler, supports_trailing_status=True):
|
||||
super(Jtagice3Protocol, self).__init__(transport, handler)
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Created JTAGICE3 protocol")
|
||||
self.supports_trailing_status = supports_trailing_status
|
||||
|
||||
def check_response(self, response, expected=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks the response for known errors
|
||||
|
||||
:param response: response bytes
|
||||
:param expected: expected response
|
||||
:return: data from response
|
||||
"""
|
||||
status, data = self.peel_response(response, expected)
|
||||
if not status:
|
||||
error_message = self.error_as_string(data[0])
|
||||
msg = "JTAGICE3 error response code 0x{:02X}: '{:s}' ".format(data[0], error_message)
|
||||
self.logger.error(msg)
|
||||
raise Jtagice3ResponseError(error_message, data[0])
|
||||
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
def error_as_string(self, code):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the response error as a string (error code translated to descriptive string)
|
||||
|
||||
:param code: error code
|
||||
:return: error code as descriptive string
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return self.JTAGICE3_ERRORS[code]
|
||||
except KeyError:
|
||||
return "Unknown error!"
|
||||
|
||||
def peel_response(self, response, expected=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Process the response, extracting error codes and data
|
||||
|
||||
:param response: raw response bytes
|
||||
:param expected: expected response
|
||||
:return: status, data
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return_list = False, [0xFF]
|
||||
# Special handling
|
||||
if expected is not None and response[0] == expected:
|
||||
return_list = True, response[2:]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if response[0] == self.PROTOCOL_OK:
|
||||
return_list = True, []
|
||||
elif response[0] == self.PROTOCOL_LIST:
|
||||
return_list = True, response[2:]
|
||||
elif response[0] == self.PROTOCOL_DATA:
|
||||
# Trailing status is not included on some handlers
|
||||
if self.supports_trailing_status and response[-1] == self.FAILURE_OK:
|
||||
return_list = True, response[2:-1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return_list = False, [response[-1]]
|
||||
elif response[0] == self.PROTOCOL_FAILED:
|
||||
return_list = False, [response[2]]
|
||||
|
||||
return return_list
|
||||
|
||||
def query(self, context):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Queries functionality using the QUERY API
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: Query context
|
||||
:return: List of supported entries
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Query to context 0x{:02X}".format(context))
|
||||
resp = self.jtagice3_command_response([self.CMD_QUERY, self.CMD_VERSION0, context])
|
||||
status, data = self.peel_response(resp)
|
||||
if not status:
|
||||
msg = "Unable to QUERY (failure code 0x{:02X})".format(data[0])
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError(msg)
|
||||
return data
|
||||
|
||||
def set_byte(self, context, offset, value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sets a single byte parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:param value: value to set
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._set_protocol(context, offset, bytearray([value]))
|
||||
|
||||
def set_le16(self, context, offset, value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sets a little-endian 16-bit parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:param value: value to set
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._set_protocol(context, offset, binary.pack_le16(value))
|
||||
|
||||
def set_le32(self, context, offset, value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Sets a little-endian 32-bit parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:param value: value to set
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._set_protocol(context, offset, binary.pack_le32(value))
|
||||
|
||||
def _set_protocol(self, context, offset, data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generic function for setting parameters
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:param data: values to set
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("JTAGICE3::set {:d} byte(s) to context {:d} offset {:d}".format(len(data),
|
||||
context,
|
||||
offset))
|
||||
resp = self.jtagice3_command_response(
|
||||
bytearray([self.CMD_SET, self.CMD_VERSION0, context, offset, len(data)]) + data)
|
||||
resp_status, resp_data = self.peel_response(resp)
|
||||
if not resp_status:
|
||||
msg = "Unable to SET (failure code 0x{:02X})".format(resp_data[0])
|
||||
raise PyedbglibError(msg)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_byte(self, context, offset):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get a single-byte parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:return: value read
|
||||
"""
|
||||
data = self._get_protocol(context, offset, 1)
|
||||
return data[0]
|
||||
|
||||
def get_le16(self, context, offset):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get a little-endian 16-bit parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:return: value read
|
||||
"""
|
||||
data = self._get_protocol(context, offset, 2)
|
||||
return binary.unpack_le16(data)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_le32(self, context, offset):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get a little-endian 32-bit parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:return: value read
|
||||
"""
|
||||
data = self._get_protocol(context, offset, 4)
|
||||
return binary.unpack_le32(data)
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_protocol(self, context, offset, numbytes):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generic function to get a parameter
|
||||
|
||||
:param context: context (address) to set
|
||||
:param offset: offset address to set
|
||||
:param numbytes: number of bytes to get
|
||||
:return: value read
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.logger.debug("JTAGICE3::get {:d} byte(s) from context {:d} offset {:d}".format(numbytes, context, offset))
|
||||
resp = self.jtagice3_command_response([self.CMD_GET, self.CMD_VERSION0, context, offset, numbytes])
|
||||
status, data = self.peel_response(resp)
|
||||
if not status:
|
||||
msg = "Unable to GET (failure code 0x{:02X})".format(data[0])
|
||||
raise Jtagice3ResponseError(msg, data)
|
||||
return data
|
||||
21
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pyedbglib/pyedbglib_errors.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
pyedbglib specific exceptions
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
class PyedbglibError(Exception):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Base class for all pyedbglib specific exceptions
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, msg=None, code=0):
|
||||
super(PyedbglibError, self).__init__(msg)
|
||||
self.code = code
|
||||
|
||||
class PyedbglibNotSupportedError(PyedbglibError):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Signals that an attempted operation is not supported
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, msg=None, code=0):
|
||||
super(PyedbglibNotSupportedError, self).__init__(msg)
|
||||
self.code = code
|
||||
146
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pyedbglib/util/binary.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
|
||||
"""Packing and unpacking numbers into bytearrays of 8-bit values with various endian encodings"""
|
||||
|
||||
from numbers import Integral
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_input_value(value, bits):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: An integer
|
||||
:param bits: Number of bits used to represent this integer
|
||||
:return: Raises an OverflowError if the value is too large
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Be sure to support both py2 and py3
|
||||
if not isinstance(value, Integral):
|
||||
raise TypeError("The input {} is not an Integral type".format(value))
|
||||
|
||||
if value > (2 ** bits) - 1:
|
||||
raise OverflowError("Value {} is larger than the maximum value {}".format(value, (2 ** bits) - 1))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_le32(value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: input value
|
||||
:return: 32-bit little endian bytearray representation of the input value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_value(value, 32)
|
||||
return bytearray([value & 0xFF, (value >> 8) & 0xFF, (value >> 16) & 0xFF, (value >> 24) & 0xFF])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_be32(value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: input value
|
||||
:return: 32-bit big endian bytearray representation of the input value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_value(value, 32)
|
||||
return bytearray(
|
||||
[(value >> 24) & 0xFF,
|
||||
(value >> 16) & 0xFF,
|
||||
(value >> 8) & 0xFF,
|
||||
value & 0xFF])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_le24(value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: input value
|
||||
:return: 24-bit little endian bytearray representation of the input value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_value(value, 24)
|
||||
return bytearray([value & 0xFF, (value >> 8) & 0xFF, (value >> 16) & 0xFF])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_be24(value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: input value
|
||||
:return: 24-bit big endian bytearray representation of the input value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_value(value, 24)
|
||||
return bytearray(
|
||||
[(value >> 16) & 0xFF,
|
||||
(value >> 8) & 0xFF,
|
||||
value & 0xFF])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_le16(value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: input value
|
||||
:return: 16-bit little endian bytearray representation of the input value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_value(value, 16)
|
||||
return bytearray([value & 0xFF, (value >> 8) & 0xFF])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_be16(value):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param value: input value
|
||||
:return: 16-bit big endian bytearray representation of the input value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_value(value, 16)
|
||||
return bytearray([(value >> 8) & 0xFF, value & 0xFF])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _check_input_array(data, length):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Used to check if a bytearray or list of 8-bit values has the correct length to convert to an integer
|
||||
|
||||
:param data: bytearray (or list) representing a value
|
||||
:param length: Expected length of the list
|
||||
:return: Raises a ValueError if len(data) is not the same as length
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not isinstance(data, (list, bytearray)):
|
||||
raise TypeError("The input {} is not a list of bytearray".format(data))
|
||||
|
||||
if len(data) != length:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Input data {} does not have length {}".format(data, length))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpack_le32(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param data: 32-bit little endian bytearray representation of an integer
|
||||
:return: integer value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_array(data, 4)
|
||||
return data[0] + (data[1] << 8) + (data[2] << 16) + (data[3] << 24)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpack_be32(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param data: 32-bit big endian bytearray representation of an integer
|
||||
:return: integer value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_array(data, 4)
|
||||
return data[3] + (data[2] << 8) + (data[1] << 16) + (data[0] << 24)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpack_le24(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param data: 24-bit little endian bytearray representation of an integer
|
||||
:return: integer value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_array(data, 3)
|
||||
return data[0] + (data[1] << 8) + (data[2] << 16)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpack_be24(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param data: 24-bit big endian bytearray representation of an integer
|
||||
:return: integer value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_array(data, 3)
|
||||
return data[2] + (data[1] << 8) + (data[0] << 16)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpack_le16(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param data: 16-bit little endian bytearray representation of an integer
|
||||
:return: integer value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_array(data, 2)
|
||||
return data[0] + (data[1] << 8)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpack_be16(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param data: 16-bit big endian bytearray representation of an integer
|
||||
:return: integer value
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_check_input_array(data, 2)
|
||||
return data[1] + (data[0] << 8)
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
"""Generating string representations of variables for nice printouts"""
|
||||
|
||||
def bytelist_to_hex_string(bytelist):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
:param bytelist: list of byte values
|
||||
:return: String representation of the bytelist with each item as a byte value on the format 0xXX
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return '[' + ', '.join("0x%02X" % x for x in bytelist) + ']'
|
||||
81
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pymcuprog/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Python MCU programmer utility
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
pymcuprog is a utility for programming various Microchip MCU devices using Microchip CMSIS-DAP based debuggers
|
||||
|
||||
pymcuprog can be used as a library using its "backend API". For example:
|
||||
|
||||
Setup logging - pymcuprog uses the Python logging module
|
||||
>>> import logging
|
||||
>>> logging.basicConfig(format="%(levelname)s: %(message)s", level=logging.WARNING)
|
||||
|
||||
Configure the session:
|
||||
>>> from pymcuprog.backend import SessionConfig
|
||||
>>> sessionconfig = SessionConfig("atmega4808")
|
||||
|
||||
Instantiate USB transport (only 1 tool connected)
|
||||
>>> from pymcuprog.toolconnection import ToolUsbHidConnection
|
||||
>>> transport = ToolUsbHidConnection()
|
||||
|
||||
Instantiate backend
|
||||
>>> from pymcuprog.backend import Backend
|
||||
>>> backend = Backend()
|
||||
|
||||
Connect to tool using transport
|
||||
>>> backend.connect_to_tool(transport)
|
||||
|
||||
Start the session
|
||||
>>> backend.start_session(sessionconfig)
|
||||
|
||||
Read the target device_id
|
||||
>>> device_id = backend.read_device_id()
|
||||
>>> print ("Device ID is {0:06X}".format(int.from_bytes(d, byteorder="little")))
|
||||
|
||||
Print the pymcuprog package version:
|
||||
>>> from pymcuprog.version import VERSION as pymcuprog_version
|
||||
>>> print("pymcuprog version {}".format(pymcuprog_version))
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, the CLI-backend API is versioned for convenience:
|
||||
>>> print("pymcuprog backend API version: {}".format(backend.get_api_version()))
|
||||
|
||||
Logging
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
This package uses the Python logging module for publishing log messages to library users.
|
||||
A basic configuration can be used (see example), but for best results a more thorough configuration is
|
||||
recommended in order to control the verbosity of output from dependencies in the stack which also use logging.
|
||||
See logging.yaml which is included in the package (although only used for CLI)
|
||||
|
||||
Dependencies
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
pymcuprog depends on pyedbglib for its transport protocol.
|
||||
pyedbglib requires a USB transport library like libusb. See pyedbglib package for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported devices and tools
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
Note: pymcuprog is primarily intended for use with PKOB nano (nEDBG) debuggers which
|
||||
are found on Curiosity Nano kits and other development boards. This means that it is
|
||||
continuously tested with a selection of AVR devices with UPDI interface as well as a
|
||||
selection of PIC devices. However since the protocol is compatible between all
|
||||
EDBG-based debuggers (pyedbglib) it is possible to use pymcuprog with a wide range of
|
||||
debuggers and devices, although not all device families/interfaces have been implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
The following Atmel/Microchip debuggers are supported:
|
||||
* JTAGICE3 (only firmware version 3.x)
|
||||
* Atmel-ICE
|
||||
* Power Debugger
|
||||
* EDBG
|
||||
* mEDBG
|
||||
* PKOB nano (nEDBG)
|
||||
* MPLAB PICkit 4 ICD (only when in 'AVR mode')
|
||||
* MPLAB Snap ICD (only when in 'AVR mode')
|
||||
|
||||
Not all functionality is provided on all boards. See device support below.
|
||||
|
||||
The following device-types are supported:
|
||||
* All UPDI devices, whether mounted on kits or standalone
|
||||
* PIC devices mounted on Curiosity Nano kits, or similar board with PKOB nano (nEDBG) debugger
|
||||
* Other devices (eg ATmega328P, ATsamd21e18a) may be partially supported for experimental purposes
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
logging.getLogger(__name__).addHandler(logging.NullHandler())
|
||||
658
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pymcuprog/backend.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,658 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Backend interface for the pymcuprog utility.
|
||||
|
||||
This module is the boundary between the Command Line Interface (CLI) part and
|
||||
the backend part that does the actual job. Any external utility or script that
|
||||
needs access to the functionality provided by pymcuprog should connect to the
|
||||
interface provided by this backend module
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Python 3 compatibility for Python 2
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
# pyedbglib dependencies
|
||||
from pyedbglib.hidtransport.hidtransportfactory import hid_transport
|
||||
from pyedbglib.hidtransport.hidtransportbase import HidTransportBase
|
||||
from pyedbglib.protocols import housekeepingprotocol
|
||||
from pyedbglib.protocols.jtagice3protocol import Jtagice3ResponseError
|
||||
|
||||
from .pymcuprog_errors import PymcuprogToolConfigurationError, PymcuprogToolConnectionError
|
||||
from .pymcuprog_errors import PymcuprogNotSupportedError, PymcuprogEraseError
|
||||
from .pymcuprog_errors import PymcuprogSessionConfigError, PymcuprogSessionError
|
||||
from .programmer import Programmer
|
||||
from .deviceinfo import deviceinfo
|
||||
from .deviceinfo.memorynames import MemoryNames
|
||||
from .deviceinfo.memorynames import MemoryNameAliases
|
||||
from .deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
from .deviceinfo.deviceinfokeys import DeviceInfoKeys, DeviceMemoryInfoKeys
|
||||
from .toolconnection import ToolUsbHidConnection, ToolSerialConnection
|
||||
from .utils import read_tool_info
|
||||
from .utils import read_target_voltage, read_supply_voltage_setpoint, read_usb_voltage
|
||||
from .utils import set_supply_voltage_setpoint
|
||||
from .hexfileutils import read_memories_from_hex
|
||||
|
||||
# Files in devices folder not representing devices
|
||||
NON_DEVICEFILES = ["__init__.py"]
|
||||
DEVICE_FOLDER = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) + "//deviceinfo//devices"
|
||||
|
||||
# This class is a collection of parameters so no need for any methods
|
||||
#pylint: disable=too-few-public-methods
|
||||
class SessionConfig(object):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Collection of all parameters needed when configuring a programming session
|
||||
|
||||
Used as input parameter for the start_session function
|
||||
"""
|
||||
device = None
|
||||
interface = None
|
||||
# For some interfaces this is baud in bits per second and for other interfaces this is clock frequency in Hz
|
||||
interface_speed = None
|
||||
# Path to python devicesupportscripts for PIC devices
|
||||
packpath = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Content and format of special_options will depend on the device stack implementation.
|
||||
# Normally these options are not in use.
|
||||
special_options = None
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, device):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
device name is mandatory
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.device = device
|
||||
|
||||
# To achieve a single entry point for users of the backend part of pymcuprog it is accepted to exceed the maximum
|
||||
# number of methods.
|
||||
#pylint: disable=too-many-public-methods
|
||||
class Backend(object):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Backend interface of the pymcuprog utility.
|
||||
This class provides access to all the functionality provided by pymcuprog
|
||||
"""
|
||||
API_VERSION = '2.0'
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
# Hook onto logger
|
||||
self.logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
self.transport = None
|
||||
self.connected_to_tool = False
|
||||
self.session_active = False
|
||||
self.programmer = None
|
||||
self.device_memory_info = None
|
||||
self.housekeeper = None
|
||||
|
||||
def get_api_version(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the current pymcuprog API version
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.API_VERSION
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def get_supported_devices():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Return a list of devices supported by pymcuprog.
|
||||
|
||||
This will be the list of devices with a corresponding device file
|
||||
:returns: List of device names
|
||||
"""
|
||||
devices = []
|
||||
for filename in os.listdir(DEVICE_FOLDER):
|
||||
if filename not in NON_DEVICEFILES and filename.endswith('.py'):
|
||||
devices.append(filename.split('.py')[0])
|
||||
|
||||
return devices
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def get_available_hid_tools(serialnumber_substring='', tool_name=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Return a list of Microchip USB HID tools (debuggers) connected to the host
|
||||
|
||||
:param serialnumber_substring: can be an empty string or a subset of a serial number. Not case sensitive
|
||||
This function will do matching of the last part of the devices serial numbers to
|
||||
the serialnumber_substring. Examples:
|
||||
'123' will match "MCHP3252000000043123" but not "MCP32520001230000000"
|
||||
'' will match any serial number
|
||||
:param tool_name: tool type to connect to. If None any tool matching the serialnumber_substring
|
||||
will be returned
|
||||
:returns: List of pyedbglib.hidtransport.hidtransportbase.HidTool objects
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Just use a temporary transport as the request is only to report connected Microchip HID tools,
|
||||
# not to connect to any of them
|
||||
transport = hid_transport()
|
||||
|
||||
return transport.get_matching_tools(serialnumber_substring, tool_name)
|
||||
|
||||
def connect_to_tool(self, toolconnection):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Connect to a tool
|
||||
|
||||
The tool can either be a USB HID tool or a serial port.
|
||||
:param ToolConnection: This is an instance of one of the ToolConnection sub-classes. This object wraps
|
||||
parameters needed to identify which tool to connect to like tool name and USB serial or serial port
|
||||
name (e.g. 'COM1').
|
||||
|
||||
For USB HID tools there are some special handling:
|
||||
- If both tool name and usb_serial are None any tool will be picked.
|
||||
- If usb_serial is None any tool matching the tool name will be picked
|
||||
- If tool name is None any tool matching the usb_serial will be picked
|
||||
- If more than one tool is connected that matches the tool name and usb_serial parameters a
|
||||
PymcuprogToolConnectionError exception will be raised.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if more than one matching tool is found or if no matching tool is found
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConfigurationError if the toolconnection configuration is incorrect
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(toolconnection, ToolSerialConnection):
|
||||
# For serial port connection no connection action is needed, just need to store the
|
||||
# Serial port number to be used (e.g. 'COM1')
|
||||
self.transport = toolconnection.serialport
|
||||
elif isinstance(toolconnection, ToolUsbHidConnection):
|
||||
self.transport = hid_transport()
|
||||
connect_status = False
|
||||
try:
|
||||
connect_status = self.transport.connect(serial_number=toolconnection.serialnumber,
|
||||
product=toolconnection.tool_name)
|
||||
except IOError as error:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogToolConnectionError("Unable to connect to USB device ({})".format(error))
|
||||
|
||||
if not connect_status:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogToolConnectionError("Unable to connect to USB device")
|
||||
|
||||
self.housekeeper = housekeepingprotocol.Jtagice3HousekeepingProtocol(self.transport)
|
||||
self.housekeeper.start_session()
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogToolConfigurationError("Unknown toolconnection argument type: {})".
|
||||
format(type(toolconnection)))
|
||||
|
||||
self.connected_to_tool = True
|
||||
|
||||
def disconnect_from_tool(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Disconnect the connected tool
|
||||
|
||||
If no tool is connected nothing is done (i.e. no exception raised when not connected)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self._is_connected_to_hid_tool():
|
||||
self.housekeeper.end_session()
|
||||
self.transport.disconnect()
|
||||
|
||||
self.connected_to_tool = False
|
||||
|
||||
def read_tool_info(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Interrogates tool (debugger) for useful info
|
||||
|
||||
:returns: Dictionary with various info about the connected debugger
|
||||
|
||||
:raises PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any USB HID tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
return read_tool_info(self.housekeeper)
|
||||
|
||||
def read_kit_device(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Read out the device name from kit configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
If the connected tool does not have any kit configuration
|
||||
(i.e. the tool is not an onboard debugger) None will be returned.
|
||||
connect_to_tool must have been called before calling read_kit_device, but start_session is not necessary.
|
||||
Typically read_kit_device is used to get the device name required to configure a session before calling
|
||||
start_session.
|
||||
:returns: Name of target device as given by the kit, None if the tool does not have any device configured.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any USB HID tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
dap_info = read_tool_info(self.housekeeper)
|
||||
|
||||
device_name = dap_info['device_name'].lower()
|
||||
|
||||
if device_name == '':
|
||||
device_name = None
|
||||
|
||||
return device_name
|
||||
|
||||
def read_target_voltage(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Read target voltage
|
||||
|
||||
:returns: Measured target voltage
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogNotSupportedError if the tool does not have supply capabilities
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
voltage = read_target_voltage(self.housekeeper)
|
||||
except Jtagice3ResponseError:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogNotSupportedError("Connected debugger/board does not have target voltage read capability")
|
||||
|
||||
return voltage
|
||||
|
||||
def read_supply_voltage_setpoint(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Read tool power supply voltage setpoint
|
||||
|
||||
:returns: Tool power supply voltage setpoint
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogNotSupportedError if the tool does not have supply capabilities
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
voltage = read_supply_voltage_setpoint(self.housekeeper)
|
||||
except Jtagice3ResponseError:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogNotSupportedError("Connected debugger/board does not have supply voltage capability.")
|
||||
|
||||
return voltage
|
||||
|
||||
def read_usb_voltage(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Read USB voltage
|
||||
|
||||
:returns: Measured USB voltage
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogNotSupportedError if the tool can't measure USB voltage
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
voltage = read_usb_voltage(self.housekeeper)
|
||||
except Jtagice3ResponseError:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogNotSupportedError("Connected debugger/board does not have USB voltage read capability.")
|
||||
|
||||
return voltage
|
||||
|
||||
def set_supply_voltage_setpoint(self, setpoint):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Set tool power supply voltage setpoint
|
||||
|
||||
:param setpoint: Power supply setpoint
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogNotSupportedError if the tool does not have supply capabilities
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if the setpoint is out of range
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
set_supply_voltage_setpoint(self.housekeeper, setpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reboot_tool(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Trigger a reboot of the tool (debugger)
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
self.housekeeper.end_session(reset_tool=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# A tool reboot will automatically disconnect the tool. Calling self.disconnect_from_tool
|
||||
# would just fail as it would try to talk to a tool while it is rebooting
|
||||
self.connected_to_tool = False
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def get_device_info(device):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get info about a device
|
||||
|
||||
:param device: Name of the device
|
||||
:returns: dictionary with device info as defined in the device files in pymcuprog.deviceinfo.devices
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogNotSupportedError if device is not supported
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
info = deviceinfo.getdeviceinfo(device)
|
||||
except ModuleNotFoundError:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogNotSupportedError("No device info for device: {}".format(device))
|
||||
|
||||
return info
|
||||
|
||||
def start_session(self, sessionconfig, user_interaction_callback=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Start a programming session.
|
||||
|
||||
This function will build the device model stack and initialize the tool for a
|
||||
programming session. If a session is already started calling start_session will do an end_session and start
|
||||
a new session from scratch.
|
||||
|
||||
Note connect_to_tool must have been called before start_session is called. If not an exception will be thrown.
|
||||
|
||||
:param sessionconfig: SessionConfig object wrapping the parameters configuring the session
|
||||
:param user_interaction_callback: Callback to be called when user interaction is required,
|
||||
for example when doing UPDI high-voltage activation with user target power toggle.
|
||||
This function could ask the user to toggle power and halt execution waiting for the user
|
||||
to respond (this is default behavior if the callback is None), or if the user is another
|
||||
script it could toggle power automatically and then return.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionConfigError if starting the session failed due to incorrectly configured session
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogDeviceLockedError if unable to start the session due to the device being locked
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogNotSupportedError if configured device is not supported
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that all session configuration parameters required are in place
|
||||
if sessionconfig.device is None or sessionconfig.device == '':
|
||||
raise PymcuprogSessionConfigError("Device must be specified")
|
||||
|
||||
if self.session_active:
|
||||
# A session is already active so it must be ended before starting a new session
|
||||
self.end_session()
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup the programmer
|
||||
self.programmer = Programmer(self.transport)
|
||||
|
||||
if sessionconfig.special_options is not None:
|
||||
self.programmer.set_options(sessionconfig.special_options)
|
||||
|
||||
# Try to build the stack for this device
|
||||
self.programmer.load_device(sessionconfig.device)
|
||||
|
||||
self.programmer.setup_device(
|
||||
sessionconfig.interface,
|
||||
sessionconfig.packpath,
|
||||
sessionconfig.interface_speed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make contact
|
||||
self.programmer.start(user_interaction_callback=user_interaction_callback)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get device memory info
|
||||
self.device_memory_info = self.programmer.get_device_memory_info()
|
||||
|
||||
self.session_active = True
|
||||
|
||||
def end_session(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
End a programming session
|
||||
|
||||
This will take down the device model stack and stop the programming session on the tool. However the tool will
|
||||
not be disconnected and it will be possible to do another start_session without another connect_to_tool call.
|
||||
If no session has been started this function will do nothing (i.e. it won't fail even if a session has
|
||||
not been started)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.session_active:
|
||||
# Lower the flag first to ensure it is updated as the rest of this function might fail with an exception
|
||||
# for example if UPDI were disabled during the session
|
||||
self.session_active = False
|
||||
self.programmer.stop()
|
||||
|
||||
def read_device_id(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Read out the device id
|
||||
|
||||
:return Byte array with device ID as raw byte values. Number of bytes will depend upon target type
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
return self.programmer.read_device_id()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def erase(self, memory_name=MemoryNameAliases.ALL, address=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Erase target device memory
|
||||
|
||||
If a single memory is specified it will only be erased if it won't affect other memories
|
||||
:param memory: name of memory to erase. To unlock a device use the MemoryNameAliases.ALL
|
||||
MemoryNameAliases.ALL run the widest erase:
|
||||
- For PIC the widest bulk erase will be run.
|
||||
- For AVR a chip erase will be run
|
||||
- The following memories will not be erased:
|
||||
- AVR fuses
|
||||
- EEPROM if EESAVE fuse is set for AVR
|
||||
- EEPROM if the target device does not support EEPROM erase
|
||||
- EEPROM if Data Code Protection (CPD_n) is not enabled for PIC
|
||||
- PIC ICD memory (special memory used for Debug Executives)
|
||||
:param address: optional address for erase command. If address is None the complete memory
|
||||
segment will be erased. Note that the address parameter will just propagate through the stack down to the
|
||||
device dependent implementation (devicesupportscripts for PIC and firmware for AVR). Normal use is to
|
||||
leave the address as None.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if the specified memory is not defined for the target device
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogEraseError if the memory can't be erased or if the memory can't be erased without affecting
|
||||
other memories
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
if memory_name is not None and memory_name != MemoryNameAliases.ALL:
|
||||
if not self.is_isolated_erase_possible(memory_name):
|
||||
message = "{} memory can't be erased or can't be erased without side effect".format(memory_name)
|
||||
raise PymcuprogEraseError(message)
|
||||
|
||||
self.programmer.erase(memory_name, address)
|
||||
|
||||
def is_isolated_erase_possible(self, memory_name):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Can the memory be erased without affecting other memories?
|
||||
|
||||
:param memory_name: name of memory
|
||||
:return: True only if the memory can be erased without side effects, False if memory can't be erased at all or
|
||||
if erasing it will erase other memories too.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises ValueError if memory is not defined for the configured device
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# The device model must have been loaded upfront
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
meminfo = self.device_memory_info.memory_info_by_name(memory_name)
|
||||
isolated_erase_key = DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ISOLATED_ERASE
|
||||
if isolated_erase_key in meminfo:
|
||||
return meminfo[isolated_erase_key] is True
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.error('%s flag not found for %s memory', isolated_erase_key, memory_name)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def get_chiperase_effect(self, memory_name):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the effect of a chip erase (widest bulk erase) on the given memory
|
||||
|
||||
:param memory_name: name of memory
|
||||
:return: One of the values defined by deviceinfo.eraseflags.ChiperaseEffect depending upon the settings in the
|
||||
device model for the configured device. If the chiperase_effect flag is missing in the device model
|
||||
ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises ValueError if memory is not defined for the configured device
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# The device model must have been loaded upfront
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
meminfo = self.device_memory_info.memory_info_by_name(memory_name)
|
||||
chiperase_effect_key = DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.CHIPERASE_EFFECT
|
||||
if chiperase_effect_key in meminfo:
|
||||
return meminfo[chiperase_effect_key]
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.error('%s flag not found for %s memory', chiperase_effect_key, memory_name)
|
||||
return ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED
|
||||
|
||||
def read_memory(self, memory_name=MemoryNameAliases.ALL, offset_byte=0, numbytes=0, max_chunk_size=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Read target device memory
|
||||
|
||||
:param memory_name: Name of memory as defined in memorynames.py. MemoryNameAliases.ALL reads all memories
|
||||
defined in the device model (numbytes and offset_byte will be ignored).
|
||||
:param offset_byte: Byte offset within memory to start reading at.
|
||||
:param numbytes: Number of bytes to read. 0 means read all memory locations from offset_byte and until end
|
||||
of memory
|
||||
:return: list of namedtuples with two fields: data and memory_info. data contains a byte array of
|
||||
raw data bytes and memory_info is a dictionary with memory information (as defined in
|
||||
deviceinfo.deviceinfo.DeviceMemoryInfo). Normally the list will contain one item, but when
|
||||
memory_name parameter is MemoryNameAliases.ALL there will be one namedtuple item per memory
|
||||
type read.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if trying to read outside the specified memory
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if the specified memory is not defined for the target device
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
return self.programmer.read_memory(memory_name=memory_name, offset=offset_byte, numbytes=numbytes, max_chunk_size=max_chunk_size)
|
||||
|
||||
def write_memory(self, data, memory_name=MemoryNames.FLASH, offset_byte=0, blocksize=0, pagewrite_delay=0):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Write target device memory
|
||||
|
||||
:param memory_name: Name of memory as defined in memorynames.py
|
||||
:param offset_byte: Byte offset within memory to start writing to.
|
||||
:param data: bytearray of raw data bytes to write
|
||||
:param blocksize: max number of bytes to send at a time. Ignored if 0 or omitted, and not passed
|
||||
to write_memory; only serialupdi supports this.
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if trying to write outside the specified memory
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if the specified memory is not defined for the target device
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
if blocksize == 0:
|
||||
self.programmer.write_memory(data=data, memory_name=memory_name, offset=offset_byte, pagewrite_delay=pagewrite_delay)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.programmer.write_memory(data=data, memory_name=memory_name, offset=offset_byte, blocksize=blocksize, pagewrite_delay=pagewrite_delay)
|
||||
|
||||
def verify_memory(self, data, memory_name=MemoryNames.FLASH, offset_byte=0, max_read_chunk=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Verify target device memory
|
||||
|
||||
:param memory_name: Name of memory as defined in DeviceMemoryInfo (deviceinfo.py)
|
||||
:param offset_byte: Byte offset within memory to start verifying at.
|
||||
:param data: bytearray of raw data bytes to verify against
|
||||
:return: boolean compare status
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if trying to verify outside the specified memory
|
||||
:raises: ValueError if the specified memory is not defined for the target device
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
return self.programmer.verify_memory(data=data, memory_name=memory_name, offset=offset_byte, max_read_chunk=max_read_chunk)
|
||||
|
||||
def hold_in_reset(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Hold target device in reset
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
self.programmer.hold_in_reset()
|
||||
|
||||
def release_from_reset(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Release target device from reset
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
self.programmer.release_from_reset()
|
||||
|
||||
# Releasing the target from reset will take it out of programming mode. In other words the session
|
||||
# is partly taken down. To keep housekeeping right and to take down the stack properly end_session
|
||||
# must be called
|
||||
self.end_session()
|
||||
|
||||
def write_hex_to_target(self, hexfile):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Write hexfile to target device
|
||||
|
||||
Note no erase will be run (i.e. memory is assumed to already be erased)
|
||||
|
||||
:param hexfile: name of file to write
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
hex_memories = read_memories_from_hex(os.path.abspath(hexfile), self.device_memory_info)
|
||||
for segment in hex_memories:
|
||||
memory_name = segment.memory_info[DeviceInfoKeys.NAME]
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Writing %s...", memory_name)
|
||||
self.write_memory(segment.data, memory_name, segment.offset)
|
||||
|
||||
def verify_hex(self, hexfile):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Verify target memory content against hexfile
|
||||
|
||||
:param hexfile: name of file to verify against
|
||||
:return: boolean compare status
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool (connect_to_tool not run)
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if a session has not been started (session_start not run)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._is_tool_not_connected_raise()
|
||||
self._is_session_not_active_raise()
|
||||
|
||||
hex_memories = read_memories_from_hex(os.path.abspath(hexfile), self.device_memory_info)
|
||||
verify_ok = True
|
||||
for segment in hex_memories:
|
||||
memory_name = segment.memory_info[DeviceInfoKeys.NAME]
|
||||
self.logger.debug("Verifying %s...", memory_name)
|
||||
segment_ok = self.verify_memory(segment.data, memory_name, segment.offset, max_read_chunk=max_read_chunk)
|
||||
if segment_ok:
|
||||
self.logger.debug("OK!")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
verify_ok = False
|
||||
|
||||
return verify_ok
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_tool_not_connected_raise(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if any tool is connected and if not raise an exception
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not self._is_connected_to_hid_tool() and not self._is_connected_to_serialport():
|
||||
raise PymcuprogToolConnectionError("Not connected to any tool")
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_hid_tool_not_connected_raise(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if a USB HID tool is connected and if not raise an exception
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogToolConnectionError if not connected to any tool
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not self._is_connected_to_hid_tool():
|
||||
raise PymcuprogToolConnectionError("Not connected to any USB HID debugger")
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_connected_to_hid_tool(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if a connection to a USB HID tool is active
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.connected_to_tool and isinstance(self.transport, HidTransportBase)
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_connected_to_serialport(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if a connection to a Serial port is active
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# For Serial port communication transport is only set to a string with the name of the serial port
|
||||
# to use (e.g. 'COM1').
|
||||
return self.connected_to_tool and isinstance(self.transport, str)
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_session_not_active_raise(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if a programming session is active and if not raise an exception
|
||||
|
||||
:raises: PymcuprogSessionError if programming session not active
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not self.session_active:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogSessionError("No programming session active")
|
||||
290
software/tools/pymcuprog/libs/pymcuprog/deviceinfo/deviceinfo.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
deviceinfo.py
|
||||
A simple Device Information service
|
||||
|
||||
Device information is stored in files named <devicename>.py in the devices sub-folder
|
||||
Each device file contains a dict of values
|
||||
These device files are [ideally] generated from DFP information by [running generate_device_info.py | hand]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Python 3 compatibility for Python 2
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
|
||||
from logging import getLogger
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.pymcuprog_errors import PymcuprogError
|
||||
from .memorynames import MemoryNames
|
||||
from .deviceinfokeys import DeviceMemoryInfoKeys, DeviceInfoKeys, DeviceInfoKeysPic
|
||||
|
||||
def getdeviceinfo(devicename):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Looks up device info for a given part
|
||||
|
||||
:param devicename: device to look up
|
||||
:return: device information dict
|
||||
"""
|
||||
logger = getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
logger.info("Looking for device %s", devicename)
|
||||
|
||||
devicename = devicename.lower()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
device_module = importlib.import_module("deviceinfo.devices.{}".format(devicename))
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# When pymcuprog is used as a package in other scripts
|
||||
# the deviceinfo module is part of the pymcuprog package
|
||||
device_module = importlib.import_module("pymcuprog.deviceinfo.devices.{}".format(devicename))
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
device_module = importlib.import_module("{}".format(devicename))
|
||||
|
||||
device_info = getattr(device_module, "DEVICE_INFO")
|
||||
|
||||
# For PIC devices there will be a default_bulk_erase_address outside any memory information
|
||||
# This address needs to be converted to byte address
|
||||
default_bulk_erase_address_byte = None
|
||||
for param in device_info:
|
||||
if param.startswith(DeviceInfoKeysPic.DEFAULT_BULK_ERASE_ADDRESS):
|
||||
# Check if it's word or byte oriented data
|
||||
mul = DeviceMemoryInfo.bytes_or_words(param)
|
||||
if mul is not None:
|
||||
default_bulk_erase_address_byte = int(device_info[param] * mul)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
default_bulk_erase_address_byte = device_info[param]
|
||||
|
||||
if default_bulk_erase_address_byte is not None:
|
||||
device_info[DeviceInfoKeysPic.DEFAULT_BULK_ERASE_ADDRESS] = default_bulk_erase_address_byte
|
||||
|
||||
return device_info
|
||||
|
||||
def get_supported_devices():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Return a list of all supported devices
|
||||
|
||||
A device is supported if it has a device model file in the devices folder
|
||||
"""
|
||||
root_folder = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
|
||||
dir_list = os.listdir(root_folder + "//devices")
|
||||
ignore_list = ['__init__.py']
|
||||
device_list = []
|
||||
for devicefile in dir_list:
|
||||
if devicefile.endswith(".py") and devicefile not in ignore_list:
|
||||
devicename = devicefile.split('.')[0]
|
||||
device_list.append(devicename)
|
||||
|
||||
return device_list
|
||||
|
||||
class DeviceMemoryInfo:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
API to fetch information about device memory segments
|
||||
"""
|
||||
def __init__(self, device_info):
|
||||
self.device = device_info
|
||||
self.memtypes = MemoryNames.get_all()
|
||||
|
||||
# hexfile_address is the start address for the memory segment in hex files.
|
||||
# PIC and ARM devices usually does not need the parameter as all locations are mapped in a single address space.
|
||||
# AVR8 devices does not map all memory types in a single address space.
|
||||
# Memory types have defined offsets in hex files as defined below
|
||||
self.avr8_hex_file_offsets = {
|
||||
MemoryNames.FLASH: 0x000000,
|
||||
MemoryNames.EEPROM: 0x810000,
|
||||
MemoryNames.FUSES: 0x820000,
|
||||
MemoryNames.LOCKBITS: 0x830000,
|
||||
MemoryNames.SIGNATURES: 0x840000,
|
||||
MemoryNames.USER_ROW: 0x850000
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# erase_address is the address for the erase of the memory.
|
||||
# Note that for PIC devices other memories might be erased in the same operation depending on the target,
|
||||
# see the programming spec for the target device.
|
||||
|
||||
# erase_address, hexfile_address, hexfile_size and verify mask are optional in the device models.
|
||||
# erase_address will be set to the memory address if it's missing.
|
||||
# Hex file address will be set to the memory address if it's missing, unless it's an AVR device where
|
||||
# the hex file offset is used instead.
|
||||
# Hex file size will be set to the memory size if it's missing except for EEPROM on PIC16 devices where
|
||||
# the hex file will contain phantom bytes so the hex file will contain twice as many EEPROM bytes as
|
||||
# the actual EEPROM in the device
|
||||
# verify_mask is set based on architecture
|
||||
self.paramtypes = [DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ADDRESS,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.SIZE,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.PAGE_SIZE,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.WRITE_SIZE,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.READ_SIZE,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.VERIFY_MASK,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ERASE_ADDRESS,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.HEXFILE_ADDRESS,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.HEXFILE_SIZE,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.CHIPERASE_EFFECT,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ISOLATED_ERASE]
|
||||
|
||||
self.mem_by_name = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# Find information about memory segments
|
||||
for param in self.device:
|
||||
for mtype in self.memtypes:
|
||||
# Does this line describe a memory location?
|
||||
if param.startswith(mtype):
|
||||
self._configure_memory_param(mtype, param)
|
||||
|
||||
# erase_address and hexfile_address are optional and should default to the value of the address parameter
|
||||
optional_params = [DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.VERIFY_MASK,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.HEXFILE_ADDRESS,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ERASE_ADDRESS,
|
||||
DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.HEXFILE_SIZE]
|
||||
for optional_param in optional_params:
|
||||
for memtype in self.mem_by_name:
|
||||
if optional_param not in self.mem_by_name[memtype]:
|
||||
# Set the verify mask based on architecture
|
||||
if optional_param == DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.VERIFY_MASK:
|
||||
verify_mask = self._get_verify_mask(self.device[DeviceInfoKeys.ARCHITECTURE], memtype)
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memtype][optional_param] = verify_mask
|
||||
# Set the hexfile_address
|
||||
elif optional_param == DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.HEXFILE_ADDRESS:
|
||||
self._add_hexfile_address(memtype, optional_param)
|
||||
# Set the hexfile_size
|
||||
elif optional_param == DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.HEXFILE_SIZE:
|
||||
self._add_hexfile_size(memtype, optional_param)
|
||||
# Set the erase_address
|
||||
elif optional_param == DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ERASE_ADDRESS:
|
||||
# By default the erase_address is the same as the address of the memory
|
||||
address = self.mem_by_name[memtype][DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ADDRESS]
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memtype][optional_param] = address
|
||||
|
||||
def _configure_memory_param(self, memorytype, param):
|
||||
# Check if it's word or byte oriented data
|
||||
mul = self.bytes_or_words(param)
|
||||
# Create a dict for the memory type if it does not exist
|
||||
if not self.mem_by_name.get(memorytype):
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype] = {DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.NAME: memorytype}
|
||||
# Parse and store parameter
|
||||
for ptype in self.paramtypes:
|
||||
if param.startswith("{}_{}".format(memorytype, ptype)):
|
||||
if mul is not None:
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][ptype] = int(self.device[param] * mul)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][ptype] = self.device[param]
|
||||
|
||||
def _add_hexfile_address(self, memorytype, paramname):
|
||||
# Inject hex file addresses for AVR memory areas
|
||||
if self.device[DeviceInfoKeys.ARCHITECTURE].startswith('avr8'):
|
||||
if memorytype in self.avr8_hex_file_offsets:
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][paramname] = self.avr8_hex_file_offsets[memorytype]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# The hexfile_address for memory types that doesn't make sense in a hex file like SRAM
|
||||
# and regular I/O space is defined to an address the other memory types will not reach
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][paramname] = 0xFFFFFF
|
||||
# All other memory types are mapped 1 to 1 in the hex file
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][paramname] = self.mem_by_name[memorytype][DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ADDRESS]
|
||||
|
||||
def _add_hexfile_size(self, memorytype, paramname):
|
||||
if self.device[DeviceInfoKeys.ARCHITECTURE].startswith('PIC16') and memorytype == MemoryNames.EEPROM:
|
||||
# For PIC16 devices there will be one phantom byte in the hex file for each EEPROM byte, so
|
||||
# the size of EEPROM in a hex file will be twice the size of the actual EEPROM memory
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][paramname] = self.mem_by_name[memorytype][DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.SIZE] * 2
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memorytype][paramname] = self.mem_by_name[memorytype][DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.SIZE]
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _get_verify_mask(architecture, memtype):
|
||||
# byte oriented memory
|
||||
mask = [0xFF]
|
||||
|
||||
# PIC16 is word addressed and has 14-bit flash, except EEPROM which is byte oriented
|
||||
if architecture == 'PIC16' and memtype not in [MemoryNames.EEPROM]:
|
||||
mask = [0xFF, 0x3F]
|
||||
|
||||
# PIC18 is word addressed and has 16-bit flash, except EEPROM which is byte oriented
|
||||
elif architecture == 'PIC18' and memtype not in [MemoryNames.EEPROM]:
|
||||
mask = [0xFF, 0xFF]
|
||||
|
||||
# PIC24 is word addressed and has 24-bit flash, except EEPROM which is word oriented
|
||||
elif architecture == 'PIC24':
|
||||
if memtype in [MemoryNames.EEPROM]:
|
||||
mask = [0xFF, 0xFF]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
mask = [0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0x00]
|
||||
|
||||
return mask
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def bytes_or_words(address_param):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Return multiplier for address parameter
|
||||
|
||||
The returned multiplier can be used to convert the address parameter to byte address
|
||||
:param address_param: Address parameter (used as key in device info dict)
|
||||
:return: Multiplier to convert the address to byte address
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if address_param.endswith("_byte") or address_param.endswith("_bytes"):
|
||||
mul = 1
|
||||
elif address_param.endswith("_word") or address_param.endswith("_words"):
|
||||
mul = 2
|
||||
else:
|
||||
mul = None
|
||||
return mul
|
||||
|
||||
def memory_info_by_address_range(self,
|
||||
start,
|
||||
stop,
|
||||
address_type=DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ADDRESS,
|
||||
size_type=DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.SIZE):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a list of all memories applicable for the address range(start, stop)
|
||||
|
||||
:param start: Start address (byte)
|
||||
:param stop: End address (byte)
|
||||
:param address_type: Selects between normal addresses and addresses used in hex files
|
||||
(address vs hexfile_address)
|
||||
:param size_type: Selects between normal size and size used in hexfiles (size vs hexfile_size)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# We do not support negative memory ranges
|
||||
if start > stop:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogError("Cannot parse reverse memory range {} to {}".format(start, stop))
|
||||
|
||||
memtypes = []
|
||||
|
||||
# Loop through all known memory types for this device
|
||||
for memtype in self.mem_by_name:
|
||||
address = self.mem_by_name[memtype][address_type]
|
||||
size = self.mem_by_name[memtype][size_type]
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if any of the addresses between start and stop is within the memory type range
|
||||
if start < address+size and stop > address:
|
||||
memtypes.append(self.mem_by_name[memtype])
|
||||
return memtypes
|
||||
|
||||
def memory_info_by_address(self,
|
||||
byte_address,
|
||||
address_type=DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.ADDRESS,
|
||||
size_type=DeviceMemoryInfoKeys.SIZE):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns information about the memory type for a given byte address
|
||||
|
||||
:param byte_address: Memory address to check
|
||||
:param address_type: Selects between normal addresses and addresses used in hex files
|
||||
(ADDRESS vs HEXFILE_ADDRESS)
|
||||
:param size_type: Selects between normal size and size used in hexfiles (size vs hexfile_size)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
memtype = None
|
||||
for memory in self.mem_by_name:
|
||||
if self.mem_by_name[memory][address_type] <= byte_address < \
|
||||
self.mem_by_name[memory][address_type] + self.mem_by_name[memory][size_type]:
|
||||
if memtype is not None:
|
||||
raise PymcuprogError("Duplicate memory area found for byte address '{}'".format(byte_address))
|
||||
memtype = self.mem_by_name[memory]
|
||||
return memtype
|
||||
|
||||
def memory_info_by_name(self, name):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns information about the requested memory
|
||||
"""
|
||||
memory = self.mem_by_name.get(name)
|
||||
if not memory:
|
||||
message = "Memory type '{}' not defined for device '{}'".format(name, self.device[DeviceInfoKeys.NAME])
|
||||
raise ValueError(message)
|
||||
return memory
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
||||
#pylint: disable=too-few-public-methods
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Definitions of keys for device info dictionaries
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
class DeviceInfoKeys(object):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Base class with common device info keys
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
NAME = 'name'
|
||||
ARCHITECTURE = 'architecture'
|
||||
INTERFACE = 'interface'
|
||||
DEVICE_ID = 'device_id'
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def get_all(cls):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get a list of all keys
|
||||
|
||||
:return List of all valid keys (baseclass and any subclass keys if run on a subclass)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
all_keys = []
|
||||
for attribute in dir(cls):
|
||||
if not attribute.startswith('__') and not callable(getattr(cls, attribute)):
|
||||
all_keys.append(getattr(cls, attribute))
|
||||
|
||||
return all_keys
|
||||
|
||||
class DeviceInfoKeysAvr(DeviceInfoKeys):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Keys specific to AVR device info files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
NVMCTRL_BASE = 'nvmctrl_base'
|
||||
SYSCFG_BASE = 'syscfg_base'
|
||||
OCD_BASE = 'ocd_base'
|
||||
PROG_CLOCK_KHZ = 'prog_clock_khz'
|
||||
ADDRESS_SIZE = 'address_size'
|
||||
|
||||
class DeviceInfoKeysAvr32(DeviceInfoKeys):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Keys specific to 32-bit AVR device info files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
RESET_DOMAINS = 'reset_domains'
|
||||
|
||||
class DeviceInfoKeysPic(DeviceInfoKeys):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Keys specific to PIC device info files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# This key should have _byte or _word ending in device info files to specify byte or word address
|
||||
# This ending will be removed by the getdeviceinfo function before returning the device info dictionary
|
||||
DEFAULT_BULK_ERASE_ADDRESS = 'default_bulk_erase_address'
|
||||
|
||||
class DeviceMemoryInfoKeys(object):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Keys for device memory info dictionary
|
||||
|
||||
These keys are found in the dictionaries returned by DeviceMemoryInfo for each memory type
|
||||
"""
|
||||
NAME = 'name'
|
||||
ADDRESS = 'address'
|
||||
SIZE = 'size'
|
||||
PAGE_SIZE = 'page_size'
|
||||
WRITE_SIZE = 'write_size'
|
||||
READ_SIZE = 'read_size'
|
||||
ERASE_ADDRESS = 'erase_address'
|
||||
CHIPERASE_EFFECT = 'chiperase_effect'
|
||||
ISOLATED_ERASE = 'isolated_erase'
|
||||
HEXFILE_ADDRESS = 'hexfile_address'
|
||||
HEXFILE_SIZE = 'hexfile_size'
|
||||
VERIFY_MASK = 'verify_mask'
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def get_all(cls):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get a list of all keys
|
||||
|
||||
:return List of all valid keys (baseclass and any subclass keys if run on a subclass)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
all_keys = []
|
||||
for attribute in dir(cls):
|
||||
if not attribute.startswith('__') and not callable(getattr(cls, attribute)):
|
||||
all_keys.append(getattr(cls, attribute))
|
||||
|
||||
return all_keys
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1604 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1604',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3c00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0400,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9425,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1606 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1606',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3c00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0400,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9424,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1607 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1607',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3c00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0400,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9423,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1614 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1614',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9422,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1616 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1616',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9421,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1617 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1617',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9420,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1624 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1624',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E942A,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1626 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1626',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9429,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny1627 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny1627',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x4000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9428,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny202 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny202',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0040,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f80,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9123,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny204 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny204',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0040,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f80,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9122,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny212 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny212',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0040,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f80,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9121,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny214 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny214',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0040,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f80,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9120,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny3216 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny3216',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x8000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9521,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny3217 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny3217',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0800,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x8000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9522,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny3224 devices
|
||||
The following data would normally have been collected from device packs.
|
||||
But since Microchip hasn't done this, it was deduced from device packs by Spence Konde.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny3224',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3400,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0C00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x8000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9528,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny3226 devices
|
||||
The following data would normally have been collected from device packs.
|
||||
But since Microchip hasn't done this, it was deduced from device packs by Spence Konde.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny3226',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3400,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0C00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x8000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9527,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny3227 devices
|
||||
The following data would normally have been collected from device packs.
|
||||
But since Microchip hasn't done this, it was deduced from device packs by Spence Konde.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny3227',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3400,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0C00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x8000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x80,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9526,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny402 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny402',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x1000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9227,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny404 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny404',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x1000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9226,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny406 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny406',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x1000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9225,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny412 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny412',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x1000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9223,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Required device info for the attiny414 devices
|
||||
The following data was collected from device pack Microchip.ATtiny_DFP 2.4.111
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from pymcuprog.deviceinfo.eraseflags import ChiperaseEffect
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE_INFO = {
|
||||
'name': 'attiny414',
|
||||
'architecture': 'avr8x',
|
||||
|
||||
# eeprom
|
||||
'eeprom_address_byte': 0x00001400,
|
||||
'eeprom_size_bytes': 0x0080,
|
||||
'eeprom_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'eeprom_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'eeprom_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.CONDITIONALLY_ERASED_AVR,
|
||||
'eeprom_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# fuses
|
||||
'fuses_address_byte': 0x00001280,
|
||||
'fuses_size_bytes': 0xA,
|
||||
'fuses_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'fuses_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'fuses_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# internal_sram
|
||||
'internal_sram_address_byte': 0x3f00,
|
||||
'internal_sram_size_bytes': 0x0100,
|
||||
'internal_sram_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'internal_sram_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'internal_sram_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# lockbits
|
||||
'lockbits_address_byte': 0x0000128A,
|
||||
'lockbits_size_bytes': 0x1,
|
||||
'lockbits_page_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'lockbits_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'lockbits_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# signatures
|
||||
'signatures_address_byte': 0x00001100,
|
||||
'signatures_size_bytes': 0x3,
|
||||
'signatures_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'signatures_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'signatures_write_size_bytes': 0,
|
||||
'signatures_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'signatures_isolated_erase': False,
|
||||
|
||||
# user_row
|
||||
'user_row_address_byte': 0x00001300,
|
||||
'user_row_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_page_size_bytes': 0x20,
|
||||
'user_row_read_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_write_size_bytes': 1,
|
||||
'user_row_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.NOT_ERASED,
|
||||
'user_row_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# flash
|
||||
'flash_address_byte': 0x00008000,
|
||||
'flash_size_bytes': 0x1000,
|
||||
'flash_page_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_read_size_bytes': 2,
|
||||
'flash_write_size_bytes': 0x40,
|
||||
'flash_chiperase_effect': ChiperaseEffect.ALWAYS_ERASED,
|
||||
'flash_isolated_erase': True,
|
||||
|
||||
# Some extra AVR specific fields
|
||||
'nvmctrl_base': 0x00001000,
|
||||
'syscfg_base': 0x00000F00,
|
||||
'ocd_base': 0x00000F80,
|
||||
'prog_clock_khz': 900,
|
||||
'interface': 'UPDI',
|
||||
'address_size': '16-bit',
|
||||
'device_id': 0x1E9222,
|
||||
}
|
||||